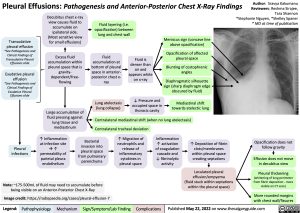
Pleural Effusions: Pathogenesis and Anterior-Posterior Chest X-Ray Findings
Decubitus chest x-ray view causes fluid to accumulate on ipsilateral side. (Most sensitive view for small effusions)
Excess fluid accumulation within pleural space that is gravity- dependent/free- flowing
Large accumulation of fluid pressing against lung tissue and mediastinum
Fluid layering (i.e. opacification) between lung and chest wall
Author: Sravya Kakumanu Reviewers: Reshma Sirajee, Tara Shannon *Stephanie Nguyen, *Shelley Spaner * MD at time of publication
Transudative
pleural effusion
*See Pathogenesis and Clinical Findings of
Transudative Pleural Effusions slide
Exudative pleural
effusion
*See Pathogenesis and Clinical Findings of
Exudative Pleural Effusions slide
Fluid accumulation at bottom of pleural space in anterior- posterior chest x- ray
Lung atelectasis (lung collapse)
Fluid is denser than air and appears white on x-ray
↓ Pressure and occupied space in thoracic cavity
Meniscus sign (concave line above opacification)
Opacification of affected pleural space
Blunting of costophrenic angles
Diaphragmatic silhouette sign (sharp diaphragm edge obscured by fluid)
Mediastinal shift towards atelectic lung
Contralateral mediastinal shift (when no lung atelectasis)
Contralateral tracheal deviation
Pleural infections
↑ Inflammation at infection site à↑ permeability of parietal pleura endothelium
Bacterial invasion into pleural space from pulmonary parenchyma
↑ Migration of neutrophils and release of inflammatory cytokines in pleural space
Inflammation ↑ activation of coagulation cascade and ↓ fibrinolytic activity
↑ Deposition of fibrin clots/membranes within pleural space creating septations
Loculated pleural effusion/empyema (fluid stuck within septations within the pleural space)
Opacification does not follow gravity
Effusion does not move in decubitus view
Pleural thickening (whitening of lung perimeter from fibrin deposition – more visible on CT scan)
More rounded margins with chest wall/fissures
Note: ~175-500mL of fluid may need to accumulate before being visible on an Anterior-Posterior Chest X-Ray
Image credit: https://radiopaedia.org/cases/pleural-effusion-7
Legend:
Pathophysiology
Mechanism
Sign/Symptom/Lab Finding
Complications
Published May 22, 2022 on www.thecalgaryguide.com
Foundations
Systems
Other Languages
Radiology Body Radiology Pleural Effusions: Pathogenesis and Anterior-Posterior Chest X-Ray Findings pleural-effusions-pathogenesis-and-anterior-posterior-chest-x-ray-findings