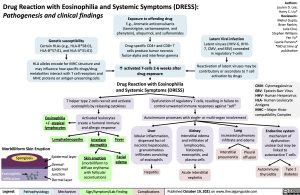
Drug Reaction with Eosinophilia and Systemic Symptoms (DRESS):
Authors: Lauren D. Lee, Harry C. Liu* Reviewers: Mehul Gupta, Brian Rankin, Julia Chai, Stephen Williams Yan Yu* Laurie Parsons* *MD at time of publication
Pathogenesis and clinical findings
Genetic susceptibility
Certain HLAs (e.g., HLA-B*58:01, HLA-B*57:01, and HLA-A*31:01)
HLA alleles encode for MHC structure and may influence how specific drugs/drug metabolites interact with T cell receptors and MHC proteins on antigen-presenting cells
Exposure to offending drug
E.g., Aromatic anticonvulsants (lamotrigine, carbamazepine, and phenytoin), allopurinol, and sulfonamides
Drug-specific CD4+ and CD8+ T cells produce tumor necrosis factor-alpha and interferon gamma
↑ activated T-cells 2-6 weeks after drug exposure
Drug Reaction with Eosinophilia and Systemic Symptoms (DRESS)
Latent Viral infection
Latent viruses (HHV-6, HHV- 7, CMV, and EBV) concealed in regulatory T-cells
Reactivation of latent viruses may be contributory or secondary to T cell activation by drugs
Eosinophilia +/- atypical lymphocytes
T helper type 2 cells recruit and activate eosinophils by releasing cytokines
Activated leukocytes create a humoral immune and allergic response
Dysfunction of regulatory T cells, resulting in failure to control unwanted immune responses against “self”
Autoimmune processes with single- or multi-organ involvement
CMV- Cytomegalovirus EBV- Epstein-Barr Virus HHV- Human Herpesvirus HLA- Human Leukocyte Antigens
MHC – Major Histo- compatibility Complex
Endocrine system
mechanism of dysfunction unclear but may be linked to autoreactive T cells
Autoimmune Type 1 thyroiditis diabetes
Lymphadenopathy
Fever
Facial edema
Liver
lobular inflammation, dispersed foci of necrotic hepatocytes, granulomatous infiltrates consisting of eosinophils
Hepatitis
Kidney
Interstitial edema and infiltrates of lymphocytes, histiocytes, eosinophils, and plasma cells
Acute interstitial nephritis
Lung
increased pulmonary infiltrate and edema
Morbilliform Skin Eruption
Spongiosis
Epidermal layer
Dermal- Epidermal Junction Dermal layer
Interface dermatitis
Skin eruption
(morbilliform to diffuse erythema with follicular accentuation)
Interstitial pneumonitis
Pleural effusion
Eosinophilic infiltration
Legend:
Pathophysiology
Mechanism
Sign/Symptom/Lab Finding
Complications
Published October 19, 2021 on www.thecalgaryguide.com
Foundations
Systems
Other Languages
Dermatology Reactive Skin Rash Drug Reaction with Eosinophilia and Systemic Symptoms (DRESS) Drug Reaction with Eosinophilia and Systemic Symptoms (DRESS)