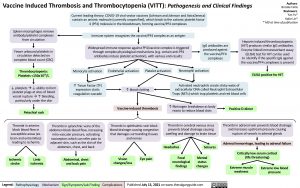
Vaccine Induced Thrombosis and Thrombocytopenia (VITT): Pathogenesis and Clinical Findings
Current leading theory: COVID-19 viral vector vaccines (Johnson and Johnson and AstraZeneca) contain an anionic molecule (currently unspecified), which binds to the cationic platelet factor 4 (PF4) molecule in the bloodstream, forming vaccine/PF4 complexes
Authors: Brooke Fallis Reviewers: Yan Yu* Katie Lin* * MD at time of publication
Spleen macrophages remove antibody/platelet complexes from circulation
Fewer unbound platelets in circulation detected on complete blood count (CBC)
Thrombocytopenia: Platelets <150x!"#/L
↓ plateletsà↓ ability to form platelet plugs at sites of blood vessel ruptureà↑ bleeding, particularly under the skin
Petechial rash
Thrombi in arteries
block blood flow in susceptible areas (ex. brain and extremities) leading to ischemia
Immune system recognizes the vaccine/PF4 complex as an antigen
Widespread immune response against PF4/vaccine complex is triggered through complex physiological mechanisms (e.g. certain anti-PF4 antibodies induce platelet activation), with various end-results:
IgG antibodies are produced against the vaccine/PF4 complexes
Heparin induced thrombocytopenia (HIT) produces similar IgG antibodies. Enzyme linked immunosorbant assay (ELISA) test for HIT can be used
to identify if the specific IgG against the vaccine/PF4 complexes is present
ELISA positive for HIT
Monocyte activation
↑ Tissue Factor (TF) expression starts coagulation cascade
Endothelial activation
Platelet activation
Neutrophil activation
Activated neutrophils create sticky webs of extracellular DNA called Neutrophil Extracellular Traps (NETs) which trap platelets and red blood cells
↑ blood clotting
Vaccine-induced thrombosis
Thrombi in ophthalmic vein block blood drainage causing congestion that damages surrounding tissues and nerves
↑ fibrinogen breakdown as body Positive D-dimer reacts to reduce blood clots
Thrombi in splanchnic veins of the abdomen block blood flow, increasing intra-vascular pressure, activating nociceptors which can refer pain to adjacent skin, such as the skin of the abdomen, chest, and back
Abdominal, chest and back pain
Thrombi in cerebral venous sinus prevents blood drainage causing swelling and damage to brain tissue
Thrombi in adrenal vein prevents blood drainage and increases upstream pressure causing rupture of vessels in adrenal glands
Adrenal hemorrhage, leading to adrenal failure
Critically low serum cortisol (life threatening)
Ischemic stroke
Limb ischemia
Vision changes/loss
Eye pain
Headaches
Focal neurological findings
Seizures
Mental status changes
Extreme muscle weakness
Extreme low blood pressure
Legend:
Pathophysiology
Mechanism
Sign/Symptom/Lab Finding
Complications
Published July 13, 2021 on www.thecalgaryguide.com
Foundations
Systems
Other Languages
Infectious Diseases Systemic Vaccine Induced Thrombosis and Thrombocytopenia (VITT): Pathogenesis and Clinical Findings VITT