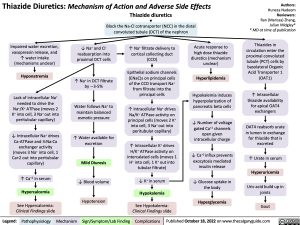
Thiazide Diuretics: Mechanism of Action and Adverse Side Effects Thiazide diuretics
Authors: Huneza Nadeem Reviewers: Ran (Marissa) Zhang, Julian Midgley* * MD at time of publication
Thiazides in circulation enter the proximal convoluted tubule (PCT) cells by basolateral Organic Acid Transporter 1 (OAT1)
↑ Intracellular thiazide availability
for apical OAT4 exchangers
OAT4 reabsorb urate in lumen in exchange
for thiazide that is excreted
↑ Urate in serum Hyperuricemia Uric acid build up in
joints Gout
Block the Na-Cl cotransporter (NCC) in the distal convoluted tubule (DCT) of the nephron
Impaired water excretion, vasopressin release, and ↑ water intake (mechanisms unclear)
Hyponatremia
Lack of intracellular Na+ needed to drive the Na+/K+ ATPase (moves 2 K+ into cell, 3 Na+ out into peritubular capillary)
↓ Intracellular Na+ drives Ca-ATPase and 3:Na:Ca exchanger activity (moves 3 Na+ into cell, 1 Ca+2 out into peritubular capillary)
↑ Ca+2 in serum
Hypercalcemia
See Hypercalcemia: Clinical Findings slide
↓ Na+ and Cl- reabsorption into proximal DCT cells
↑ Na+ in DCT filtrate by ∼3-5%
Water follows Na+ to maintain balanced osmotic pressure
↑ Water available for excretion
Mild Diuresis
↓ Blood volume Hypotension
↑ Na+ filtrate delivery to cortical collecting duct (CCD)
Epithelial sodium channels (ENaC)s on principal cells of the CCD transport Na+ from filtrate into the principal cells
↑ Intracellular Na+ drives Na/K+ ATPase activity on principal cells (moves 2 K+ into cell, 3 Na+ out into peritubular capillary)
↑ Intracellular K+ drives H/K+ ATPase activity on
intercalated cells (moves 1 H+ into cell, 1 K+ out into tubular filtrate)
↓ K+ in serum
Hypokalemia
See Hypokalemia: Clinical Findings slide
Acute response to
high dose thiazide diuretics (mechanism unclear)
Hyperlipidemia
Hypokalemia induces hyperpolarization of pancreatic beta cells
↓ Number of voltage gated Ca+2 channels
open given intracellular charge
↓ Ca+2 influx prevents exocytosis mediated insulin release
↓ Glucose uptake in the body
Hyperglycemia
Legend:
Pathophysiology
Mechanism
Sign/Symptom/Lab Finding
Complications
Published October 18, 2022 on www.thecalgaryguide.com
Foundations
Systems
Other Languages
Pharmacology Drug Action Thiazide Diuretics: Mechanism of Action and Adverse Side Effects thiazide-diuretics-mechanism-of-action-and-adverse-side-effects