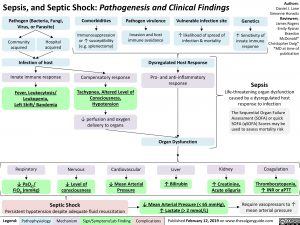
Sepsis, and Septic Shock: Pathogenesis and Clinical Findings
Authors: Daniel J. Lane Simonne Horwitz Reviewers: James Rogers Emily Ryznar Braedon McDonald* Christopher Doig* *MD at time of publication
Sepsis
Pathogen (Bacteria, Fungi, Virus, or Parasite)
Comorbidities
Immunosuppression or ↑ susceptibility (e.g. splenectomy)
Pathogen virulence
Invasion and host immune avoidance
Vulnerable infection site
↑ likelihood of spread of infection & mortality
Genetics
↑ Sensitivity of innate immune response
Community acquired
Hospital acquired
Infection of host
Innate immune response
Fever, Leukocytosis/ Leukopenia, Left Shift/ Bandemia
Compensatory response
Tachypnea, Altered Level of Consciousness, Hypotension
↓ perfusion and oxygen delivery to organs
Dysregulated Host Response
Pro- and anti-inflammatory response
Life-threatening organ dysfunction caused by a dysregulated host response to infection
The Sequential Organ Failure Assessment (SOFA) or quick
SOFA (qSOFA) Scores may be used to assess mortality risk
Respiratory
↓ PaO2 / FiO2 (mmHg)
Nervous
↓ Level of consciousness
Septic Shock
Cardiovascular
↓ Mean Arterial Pressure
Organ Dysfunction
Liver
↑ Bilirubin
Kidney
↑ Creatinine, Acute oliguria
Coagulation
Thrombocytopenia, ↑ INR or aPTT
Require vasopressors to ↑ mean arterial pressure
Persistent hypotension despite adequate fluid resuscitation
↓ Mean Arterial Pressure (< 65 mmHg), ↑ Lactate (> 2 mmol/L)
Legend:
Pathophysiology
Mechanism
Sign/Symptom/Lab Finding
Complications
Published February 12, 2019 on www.thecalgaryguide.com
Foundations
Systems
Other Languages
Infectious Diseases Systemic Sepsis, and Septic Shock: Pathogenesis and Clinical Findings Sepsis, and Septic Shock- Pathogenesis and Clinical Findings