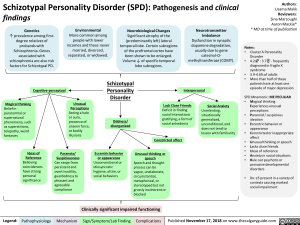
Schizotypal Personality Disorder (SPD): Pathogenesis and clinical findings
Genetics Environmental Neurobiological Changes Neurotransmitter /1` prevalence among first-More common among Significant atrophy of the Imbalance degree relatives of people with lower (predominantly left) lateral Dysfunction in synaptic probands with incomes and those never temporal lobe. Certain subregions dopamine degradation, Schizophrenia. Genes associated with married, divorced, separated, or widowed. of the prefrontal cortex have been shown to be enlarged. usually due to gene catechol-0- schizophrenia are also risk factors for Schizotypal PD. Volume 1, of specific temporal lobe subregions. methyltransferase (COMT).
Cognitive-perceptual •
Magical thinking Belief in paranormal or supernatural phenomena, such as superstitions, telepathy, weird fantasies
Unusual Perceptions Seeing a halo or aura, presence of unseen force, or bodily illusions
Ideas of Paranoia/ Reference Suspiciousness Believing Can range from coincidences persistent and have strong overt hostility, personal guardedness to significance pleasant and agreeable compliance
Schizotypal Personality Disorder Oddness/ disorganized
► Interpersonal
Lack Close Friends Deficit in finding social interactions gratifying, a form of social anhedonia
Constricted affect
Eccentric behavior Unusual thinking or or appearance speech Unconventional or Speech and thought idiosyncratic process can be hygiene, attire, or vague, unelaborate, social behaviors circumstantial, metaphorical, or stereotyped but not grossly incoherent or blocked
Social Anxiety Unrelenting, situationally generalized, unconditional, and does not tend to lessen with familiarity
Clinically significant impaired functioning
Authors: Usama Malik Reviewers: Sina Marzoughi Aaron Mackie* * MD at time of publication
Notes: • Cluster A Personality Disorder • 4.2CY : 3.7g – frequently diagnosed in fragile X syndrome • 3.9-4.6%of adults • More than half of these patients have at least one episode of major depression
SPD Mnemonic: ME PECULIAR • Magical thinking Experiences unusual perceptions • Paranoid / suspicious ideation • Eccentric behavior or appearance • Constricted or inappropriate affect • Unusual thinking or speech • Lacks close friends • Ideas of reference • Anxiety in social situations • Rule out psychotic or pervasive developmental disorders
• Dx: present in a variety of contexts causing marked social impairment