Rheumatoid Pneumoconiosis (Caplan’s Syndrome): Pathogenesis and clinical findings
Authors: Christopher Li Keerthana Pasumarthi Reviewers: Daniela Urrego, Ben Campbell, Liam Martin* * MD at time of publication
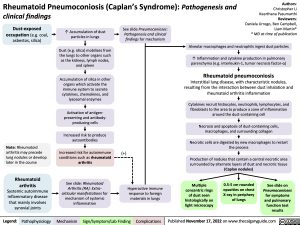
Dust-exposed occupation (e.g. coal, asbestos, silica)
↑ Accumulation of dust particles in lungs
Dust (e.g. silica) mobilizes from the lungs to other organs such as the kidneys, lymph nodes, and spleen
Accumulation of silica in other organs which activate the immune system to secrete cytokines, chemokines, and lysosomal enzymes
Activation of antigen- presenting and antibody- producing cells
Increased risk to produce autoantibodies
Increased risk for autoimmune conditions such as rheumatoid arthritis
See slide: Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA): Extra- articular manifestations for mechanism of systemic inflammation
See slide Pneumoconioses: Pathogenesis and clinical findings for mechanism
Note: Rheumatoid arthritis may precede lung nodules or develop later in the course
Rheumatoid arthritis
Systemic autoimmune inflammatory disease that mainly involves synovial joints
(+)
Alveolar macrophages and neutrophils ingest dust particles
↑ Inflammation and cytokine production in pulmonary parenchyma (e.g. interleukin-1, tumor necrosis factor-α)
Rheumatoid pneumoconiosis
Interstitial lung disease, with characteristic nodules, resulting from the interaction between dust inhalation and rheumatoid arthritis inflammation
Cytokines recruit histiocytes, neutrophils, lymphocytes, and fibroblasts to the area to produce a zone of inflammation around the dust-containing cell
Necrosis and apoptosis of dust-containing cells, macrophages, and surrounding collagen
Necrotic cells are digested by new macrophages to restart the process
Production of nodules that contain a central necrotic area surrounded by alternate layers of dust and necrotic tissue (Caplan nodules)
Hyperactive immune response to foreign materials in lungs
Multiple concentric rings of dust seen histologically on light microscopy
0.5-5 cm rounded opacities on chest X-ray in periphery of lungs
See slide on
Pneumoconioses
for symptoms and pulmonary function test results
Legend:
Pathophysiology
Mechanism
Sign/Symptom/Lab Finding
Complications
Published November 17, 2022 on www.thecalgaryguide.com
Foundations
Systems
Other Languages
Rheumatology Sero-positive Arthropathies Rheumatoid Pneumoconiosis (Caplan’s Syndrome): Pathogenesis and clinical findings rheumatoid-pneumoconiosis-caplans-syndrome-pathogenesis-and-clinical-findings