Primary Myelofibrosis: Pathogenesis and clinical findings
Legend: Published March 30, 2019 on www.Pathophysiology Mechanism Sign/Symptom/Lab Finding Complications thecalgaryguide.com
Author:
Tony Gu
Reviewers:
Naman Siddique
Sonia Cerquozzi*
Man-Chiu Poon*
* MD at time of publication
Definitions:
Constitutive activation – Constant
expression of gene
Extramedullary hematopoeisis – red
blood cell production outside of bone
marrow
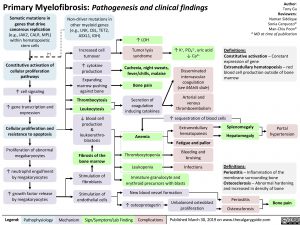
Somatic mutations in
genes that drive
cancerous replication
(e.g., JAK2, CALR, MPL)
within hematopoietic
stem cells
Non-driver mutations in
other myeloid genes
(e.g., LNK, CBL, TET2,
ASXL1, IDH)
Constitutive activation of
cellular proliferation
pathways
↑ cell signaling
↑ gene transcription and
expression
Cellular proliferation and
resistance to apoptosis
Proliferation of abnormal
megakaryocytes
↑ neutrophil engulfment
by megakaryocytes
↑ growth factor release
by megakaryocytes
Stimulation of
fibroblasts
Stimulation of
endothelial cells
New blood vessel formation
↑ osteoprotegerin Unbalanced osteoblast
proliferation Osteosclerosis
Fibrosis of the
bone marrow
Anemia
Bleeding and
bruising
Infections
Fatigue and pallor
Bone pain
Increased cell
turnover
Tumor lysis
syndrome
Cachexia, night sweats,
fever/chills, malaise
Expanding
marrow pushing
against bone
Extramedullary
hematopoiesis Hepatomegaly
Portal
hypertension
Splenomegaly
↑ LDH
Thrombocytosis
Leukocytosis
Secretion of
coagulation
inducing cytokines
Arterial and
venous
thromboembolism
↓ blood cell
production
&
leukoerythroblastosis
Thrombocytopenia
Leukopenia
↑ K+, PO4
2-, uric acid
↓ Ca2+
Bone pain
Periostitis
Immature granulocyte and
erythroid precursors with blasts
↑ cytokine
production
(+)
↑ sequestration of blood cells
Disseminated
intervascular
coagulation
(see MAHA slide)
Definitions:
Periostitis – Inflammation of the
membrane surrounding bone
Osteosclerosis – Abnormal hardening
and increased in density of bone
Foundations
Systems
Other Languages
Hematology Blood Cell Malignancies Primary Myelofibrosis: pathogenesis and clinical findings Primary Myelofibrosis pathogenesis and clinical findings