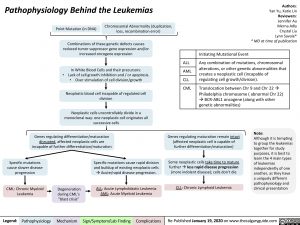
Pathophysiology Behind the Leukemias
Authors: Yan Yu, Katie Lin Reviewers: Jennifer Au Merna Adly Crystal Liu Lynn Savoie* * MD at time of publication
Point Mutation (in DNA)
Chromosomal Abnormality (duplication, loss, recombination error)
Combinations of these genetic defects causes reduced tumor suppressor gene expression and/or increased oncogene expression
Initiating Mutational Event
ALL
Any combination of mutations, chromosomal
alterations, or other genetic abnormalities that creates a neoplastic cell (incapable of regulating cell growth/division).
AML
CLL
CML
Translocation between Chr 9 and Chr 22à Philadelphia chromosome ( abnormal Chr 22)
àBCR-ABL1 oncogene (along with other genetic abnormalities)
•
In White Blood Cells and their precursors: Lack of cell growth inhibition and / or apoptosis.
• Over stimulation of cell division/growth Neoplastic blood cell incapable of regulated cell
division
Neoplastic cells uncontrollably divide in a monoclonal way: one neoplastic cell originates all successive cells
Genes regulating differentiation/maturation disrupted, affected neoplastic cells are incapable of further differentiation/maturation
Genes regulating maturation remain intact (affected neoplastic cell is capable of further differentiation/maturation)
Some neoplastic cells take time to mature furtheràless rapid disease progression (more indolent disease); cells don’t die
CLL: Chronic Lymphoid Leukemia
Note:
Although it is tempting to group the leukemias together for study purposes, it is best to learn the 4 main types of leukemias independently of one another, as they have a uniquely different pathophysiology and clinical presentation
Specific mutations cause slower disease progression
CML: Chronic Myeloid Leukemia
Degeneration during CML’s ”blast crisis”
Specific mutations cause rapid division and buildup of existing neoplastic cells àAcute/rapid disease progression.
ALL: Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia AML: Acute Myeloid Leukemia
Legend:
Pathophysiology
Mechanism
Sign/Symptom/Lab Finding
Complications
Re-Published January 19, 2020 on www.thecalgaryguide.com
Foundations
Systems
Other Languages
Hematology Blood Cell Malignancies Pathophysiology Behind The Leukemias Pathophysiology-Behind-the-Leukemias