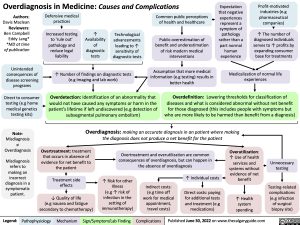
Overdiagnosis in Medicine: Causes and Complications
Expectation that negative experiences represent a symptom of pathology rather than a part normal human experience
Profit-motivated industries (e.g pharmaceutical companies)
↑ The number of diagnosed individuals serves to ↑ profits by expanding consumer base for treatments
Authors: Davis Maclean Reviewers: Ben Campbell Eddy Lang* *MD at time of publication
Unintended consequences of disease screening programs
Direct to consumer testing (e.g home medical genetics testing kits)
Note: Misdiagnosis ≠ Overdiagnosis
Misdiagnosis refers to making an incorrect diagnosis in a symptomatic patient.
Defensive medical practices
Increased testing to ‘rule out’ pathology and reduce legal liability
↑
Availability of diagnostic tests
Technological advancements leading to ↑ sensitivity of diagnostic tests
Common public perceptions of health and healthcare
Public overestimation of benefit and underestimation of risk modern medical interventions
Assumption that more medical information (e.g testing) results in better health
↑ Number of findings on diagnostic tests (e.g Imaging and lab work)
Medicalization of normal life experiences
Overdetection: Identification of an abnormality that would not have caused any symptoms or harm in the patient’s lifetime if left undiscovered (e.g detection of subsegmental pulmonary embolism)
Overdefinition: Lowering thresholds for classification of diseases and what is considered abnormal without net benefit
for those diagnosed (this includes people with symptoms but who are more likely to be harmed than benefit from a diagnosis)
Overdiagnosis: making an accurate diagnosis in an patient where making the diagnosis does not produce a net benefit for the patient
Overtreatment: treatment that occurs in absence of evidence for net benefit to the patient
Treatment side effects
↓ Quality of life
(e.g nausea and fatigue secondary to chemotherapy)
Overtreatment and overutilization are common consequences of overdiagnosis, but can happen in the absence of overdiagnosis
Overutilization: ↑ Use of health services and systems without evidence of net benefit
↑ Health system spending
Unnecessary testing
Testing-related complications (e.g infection of surgical biopsy site)
↑ Risk for other Illness
(e.g ↑ risk of infection in the setting of immunotherapy)
Indirect costs: (e.g time off work for medical appointment, travel costs)
↑ Individual costs
Direct costs: paying for additional tests and treatment (e.g medications)
Legend:
Pathophysiology
Mechanism
Sign/Symptom/Lab Finding
Complications
Published June 30, 2022 on www.thecalgaryguide.com
Foundations
Systems
Other Languages
Population Health Health Promotion & Screening Overdiagnosis in Medicine: Causes and Complications overdiagnosis-in-medicine-causes-and-complications