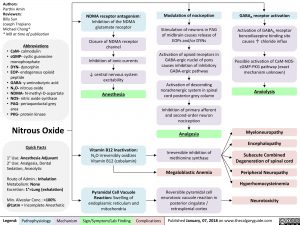
GABAAreceptor activation
Activation of GABAAreceptor benzodiazepine binding site causes ↑ chloride influx
Possible activation of Ca M – N O S- cG M P-PKG pathway (exact mechanism unknown)
Anxiolysis
Myeloneuropathy
Encephalopathy
Subacute Combined Degeneration of spinal cord
Peripheral Neuropathy
Hyperhomocysteinemia
Megaloblastic Anemia
Irreversible inhibition of methionine synthase
Modulation of nociception
Stimulation of neurons in PAG of midbrain causes release of E O Ps and/or DY N s
Activation of opioid receptors in GABA-ergicnuclei of pons causes inhibition of inhibitory GABA-ergicpathway
Activation of descending noradrenergic system in spinal cord posterior grey column
Inhibition of primary afferent and second-order neuron nociception
Analgesia
Authors: Parthiv Amin Reviewers: Billy Sun Joseph Tropiano Michael Chong* * MD at time of publication
Abbreviations •CaM-calmodulin •cGMP-cyclic guanosine monophosphate •DYN-dynorphin •EOP-endogenous opioid peptide •GABA-γ-aminobutyric acid •N2O-nitrous oxide •NDMA-N-methyl-D-aspartate •NOS-nitric oxide synthase •PAG-periaqueductal grey area •PKG-protein kinase
Nitrous Oxide
NDMA receptor antagonism: Inhibition of the N D M A glutamate receptor
Closure of NDMA receptor channel
Inhibition of ionic currents
↓ central nervous system excitability
Anesthesia
Quick Facts
1°Use: Anesthesia Adjuvant 2°Use: Analgesia, Dental Sedation, Anxiolytic
Route of Admin.: Inhalation Metabolism: None Excretion: 1°=Lung (exhalation)
Min. Alveolar Conc.: >100% @1atm = Incomplete Anesthetic
Vitamin B12 Inactivation: N2O irreversibly oxidizes Vitamin B12 (cobalamin)
Pyramidal Cell Vacuole Reaction: Swelling of endoplasmic reticulum and mitochondria
Reversible pyramidal cell neurotoxic vacuole reaction in posterior cingulate / retrosplenial cortex
Neurotoxicity
Legend:
Pathophysiology
Mechanism
Sign/Symptom/Lab Finding
Complications
Published January,07, 2018 on www.thecalgaryguide.com