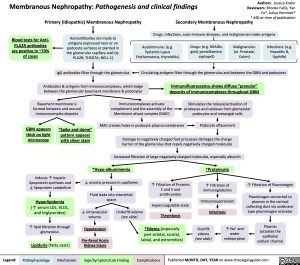
Authors: Jessica Krahn Membranous Nephropathy: Pathogenesis and clinical findings Reviewers: Brooke Fallis, Yan Yu*, Juliya Hemmet* * MD at time of publication
Primary (Idiopathic) Membranous Nephropathy
Secondary Membranous Nephropathy
Drugs, infections, auto-immune diseases, and malignancies make antigens
Blood tests for Anti- PLA2R antibodies
are positive in ~70% of cases
Autoantibodies are made to antigens expressed near or on podocyte surfaces or planted in the glomerular capillary wall (ie. PLA2R; THSD7A; NELL-1)
IgG antibodies filter through the glomerulus
Autoimmune: (e.g. Systemic Lupus Erythematous, thyroiditis)
Drugs: (e.g. NSAIDs, gold, penicillamine, captopril)
Malignancies: (ie. Prostate, Colon)
Infections: (e.g. Hepatitis B, Syphilis)
Circulating antigens filter through the glomerulus and between the GBM and podocytes
Antibodies & antigens form immunocomplexes, which lodge Immunofluorescence shows diffuse “granular”
between the glomerular basement membrane & podocytes
deposits of immunocomplexes throughout GBM
Basement membrane is formed between and around immunocomplex deposits
Immunocomplexes activate complement and the assembly of the Membrane attack complex (MAC)
MAC creates holes in podocyte plasma membranes
Stimulates the release/activation of proteases and oxidases from glomerular podocytes and mesangial cells
GBM appears thick on light microscopy
“Spike and dome” pattern appears with silver stain
Podocyte effacement
Damage to negatively charged foot processes damages the charge barrier of the glomerulus that repels negatively charged molecules
Increased filtration of large negatively charged molecules, especially albumin
Induces ↑ hepatic lipoprotein synthesis and ↓ lipoprotein catabolism
Hyperlipidemia
(↑ serum LDL, VLDL, and triglycerides)
↑ lipid filtration through glomerulus
Lipiduria (fatty casts)
*Hypo-albuminemia
↓ oncotic pressure in capillaries
Fluid leaks into interstitial space
↑ Filtration of Proteins C and S and antithrombin
Hypercoagulable state
Thrombosis *Edema (especially
*Proteinuria
↑ Filtration of immunoglobulins
Immunosuppression
Infections
↑ Filtration of Plasminogen
Plasminogen converted to plasmin in the cortical collecting duct via urokinase- type plasminogen activator
Plasmin activates the epithelial sodium channel
↓ intravascular volume
Hypotension
Pre-Renal Acute Kidney Injury
Underfill edema
(see slide)
peri-orbital, scrotal, labial, and extremities)
Overfill
edema
(see slide)
↑ Na+ and water reabsorption
Legend:
Pathophysiology
Mechanism
Sign/Symptom/Lab Finding
Complications
Published MONTH, DAY, YEAR on www.thecalgaryguide.com
Foundations
Systems
Other Languages
Nephrology Kidney Injury Membranous Nephropathy: Pathogenesis and clinical findings Membranous Nephropathy