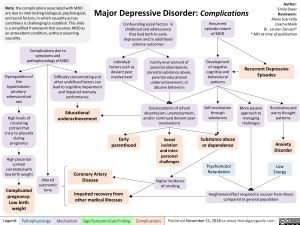
Note: the complications associated with MDD are due to interlocking biological, psychological, and social factors, in which causality across conditions is challenging to establish. This slide is a simplified framework that assumes MDD as an antecedent condition, without assuming causality.
Major Depressive Disorder: Complications
Confounding social factors in childhood and adolescence that lead both to early depression and to adulthood adverse outcomes
Complications due to symptoms and pathophysiology of MDD Individual factors such as deviant peer Dysregulation of Difficulty concentrating and involvement the other undefined factors can hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenocortical axis lead to cognitive impairment and impaired memory performance Educational High levels of circulating underachievement cortisol that cross to placenta during pregnancy Early parenthood • High placental cortisol correlated with low birth weight Coronary Artery Altered Disease autonomic Complicated tone pregnancy: Impaired recovery from Low birth weight other medical illnesses
Legend:
Pathophysiology Mechanism
Sign/Symptom/Lab Finding
Family environment of parental absenteeism, parental substance abuse, parental educational underachievement, or abusive behaviors
Recurrent episodic nature of MDD
Development of negative cognitive and behavioural patterns
Author: Emily Ower Reviewers: Alexa Scarcello Usama Malik Dr. Lauren Zanussi* * MD at time of publication
Recurrent Depressive Episodes
Social patterns of school absenteeism, unemployment, and/or continued deviant peer involvement
Social isolation and inter-personal challenges
Higher incidence of smoking
Self-medication through substances
Substance abuse or dependence
Psychomotor Retardation
Complications
More passive approach to managing challenges
Ruminative and worry thought patterns
Anxiety Disorder
Low Energy
Heightened effort required to recover from illness compared to general population