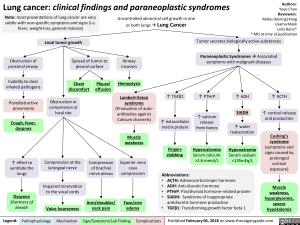
Lung cancer: clinical findings and paraneoplastic syndromes
Note: most presentations of lung cancer are very subtle with non-specific symptoms and signs (i.e. fever, weight loss, general malaise)
Obstruction of proximal airway
Inability to clear inhaled pathogens Postobstructive pneumonia
Cough, fever, dyspnea
Local tumor growth
Spread of tumor to pleural surface
Chest Pleural discomfort effusion
• Obstruction or compression at local site
Uncontrolled abnormal cell growth in one or both lungs 4 Lung Cancer
Airway invasion
Hemoptysis
Lambert-Eaton syndrome (Production of auto-antibodies against Calcium channels)
Muscle weakness
I` effort to Compression at the Compression Superior vena ventilate the laryngeal nerve of brachial cava lungs nerve plexus compression Impaired innervation to the vocal cords Dyspnea Shortness of Arm/shoulder/ Face/arm breath Voice hoarseness neck pain edema
Legend: Pathophysiology Mechanism
Sign/Symptom/Lab Finding
Authors: Yoyo Chan Reviewers: Midas (Kening) Kang Usama Malik Leila Barss* * MD at time of publication
Tumor secretes biologically active substances
Paraneoplastic Syndromes 4 Associated symptoms with malignant diseases
TGF131 extracellular matrix protein
Fingers clubbing
PTHrP T calcium release from bones
Hypercalcemia Serum calcium >2.6 mmol/L
ADH 1 SIADH T water reabsorption 1
Hyponatremia Serum sodium <135mEq/L
Abbreviations: • ACTH: Adrenocorticotropic hormone • ADH: Anti-diuretic hormone • PTHrP: Parathyroid hormone-related protein • SIADH: Syndrome of inappropriate antidiuretic hormone production • TGFI31: Transforming growth factor beta 1
1` ACTH
cortisol release and production
Cushing's syndrome (symptoms and signs caused by prolonged cortisol exposure)
Muscle weakness, hyperglycemia, severe hypokalemia