Localized Pitting Edema: Pathogenesis
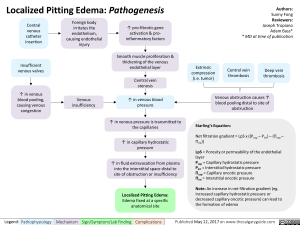
Central venous catheter insertion
-11I•
Insufficient venous valves
Foreign body irritates the endothelium, causing endothelial injury
1` pro-fibrotic gene activation & pro-inflammatory factors
Smooth muscle proliferation & thickening of the venous endothelial layer
Central vein stenosis
1` in venous blood pooling, causing venous congestion -1111. Venous insufficiency 1` in venous blood • pressure
Extrinsic compression (i.e. tumor)
Authors: Sunny Fong Reviewers: Joseph Tropiano Adam Bass* * MD at time of publication
Central vein thrombosis
Deep vein thrombosis
T in venous pressure is transmitted to the capillaries
1` in capillary hydrostatic pressure
T in fluid extravasation from plasma into the interstitial space distal to site of obstruction or insufficiency
Localized Pitting Edema: Edema fixed at a specific anatomical site
Venous obstruction causes’` blood pooling distal to site of obstruction
Starling’s Equation:
Net filtration gradient = LpS x ((Pap — Pint) Olcap
LpS = Porosity or permeability of the endothelial layer Pup = Capillary hydrostatic pressure Pint = Interstitial hydrostatic pressure ncap = Capillary oncotic pressure flint = Interstitial oncotic pressure
Note: An increase in net filtration gradient (eg. Increased capillary hydrostatic pressure or decreased capillary oncotic pressure) can lead to the formation of edema