Kallmann syndrome (KS) and Normosmic Idiopathic Hypogonadotropic Hypogonadism (nIHH): Pathogenesis and clinical findings
Authors: Danielle Lynch Reviewers: Nicola Adderley Josephine Ho* * MD at time of publication
Abbreviations:
GnRH – gonadotropin- releasing hormone
LH – luteinizing hormone FSH – follicle stimulating hormone
Notes:
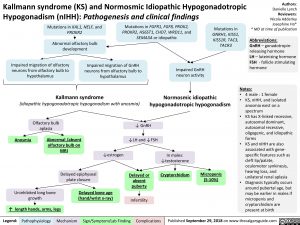
• 4 male : 1 female
• KS, nIHH, and isolated
anosmia exist on a
spectrum
• KS has X-linked recessive,
autosomal dominant, autosomal recessive,
oligogenic, and idiopathic
forms
• KS and nIHH are also
associated with gene- specific features such as
cleft lip/palate, oculomotor synkinesis, hearing loss, and unilateral renal aplasia
• Diagnosis typically occurs around pubertal age, but may be earlier in males if micropenis and cryptorchidism are present at birth
Mutations in KAL1, NELF, and PROKR2
Abnormal olfactory bulb development
Mutations in FGFR1, FGF8, PROK2, PROKR2, HS6ST1, CHD7, WRD11, and SEMA3A or idiopathic
Mutations in
GNRH1, KISS1, KISS1R, TAC3, TACR3
Impaired migration of olfactory neurons from olfactory bulb to hypothalamus
Impaired migration of GnRH neurons from olfactory bulb to hypothalamus
Impaired GnRH neuron activity
Kallmann syndrome
(idiopathic hypogonadotropic hypogonadism with anosmia)
Normosmic idiopathic hypogonadotropic hypogonadism
Anosmia
Olfactory bulb aplasia
Abnormal /absent olfactory bulb on MRI
↓ GnRH ↓LH and ↓FSH
Delayed or absent puberty
Infertility
↓estrogen
In males: ↓testosterone
Cryptorchidism
Delayed epiphyseal plate closure
Micropenis (5-10%)
Uninhibited long bone growth
↑ length hands, arms, legs
Delayed bone age (hand/wrist x-ray)
Legend:
Pathophysiology
Mechanism
Sign/Symptom/Lab Finding
Complications
Published September 29, 2018 on www.thecalgaryguide.com
Foundations
Systems
Other Languages
Pediatrics Genetic Conditions Kallmann syndrome (KS) and Normosmic Idiopathic Hypogonadotropic Hypogonadism (nIHH): Pathogenesis and clinical findings Kallmann Syndrome and Normosmotic Idiopathic Hypogonadotropism: Pathogenesis and Clinical Findings