Primary Hyperthyroidism: Pathogenesis and clinical findings
Abbreviation: TH — Thyroid hormones RAAS— Renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system TSH — Thyroid stimulating hormone
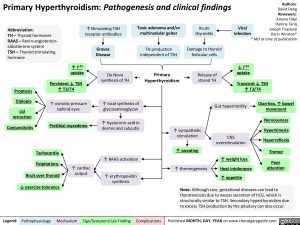
‘`Stimulating TSH receptor antibodies
Graves Disease
Toxic adenoma and/or multinodular goiter
1123 De Novo 4— synthesis of TH uptake Persistent 4, TSH Proptosis T3/T4
Lid retraction
Conjunctivitis
t osmotic pressure behind eyes
Pretibial myxedema
Tachycardia Palpitations Bruit over thyroid 4, exercise tolerance
t cardiac output
Legend: Pathophysiology Mechanism
t local synthesis of glycosaminoglycan
hyaluronic acid in dermis and subcutis
TH production independent of TSH
Acute thyroidits
Damage to thyroid follicular cells
Y Primary Hyperthyroidism
4
RAAS activation •
erythropoietin synthesis
Sign/Symptom/Lab Finding
Release of stored TH
t sympathetic stimulation
T sweating
thermogenesis
Viral infection
Authors: David Deng Reviewers: Amyna Fidai Hamna Tariq Joseph Tropiano Karin Winston* * MD at time of publication
4, 1123 uptake
Transient 4, TSH T3/T4
Gut hypermotlity –*
CNS overstimulation
Diarrhea, t bowel movement
t weight loss Heat intolerance t appetite
Nervousness
Hyperkinesia
Hyperreflexia
Tremor
Poor attention
Note: Although rare, gestational diseases can lead to thyrotoxicosis due to excess secretion of hCG, which is structurally similar to TSH. Secondary hyperthyroidism due to excess TSH production by the pituitary can also occur.
Complications I Published MONTH, DAY, YEAR on www.thecalgaryguide.com 0 GS’ I 4;