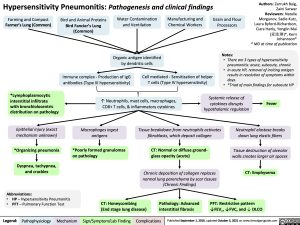
Hypersensitivity Pneumonitis: Pathogenesis and clinical findings
Authors: Zarrukh Baig, Zaini Sarwar Reviewers: Natalie Morgunov, Sadie Kutz, Laura Byford-Richardson, Ciara Hanly, Yonglin Mai (麦泳琳)*, Kerri Johannson* * MD at time of publication
Farming and Compost
Farmer’s Lung (Common)
Bird and Animal Proteins
Bird Fancier’s Lung (Common)
Water Contamination and Ventilation
Organic antigen identified by dendritic cells
Manufacturing and Chemical Workers
Grain and Flour Processors
Notes:
Immune complex – Production of IgG antibodies (Type III hypersensitivity)
Cell mediated – Sensitization of helper T cells (Type IV hypersensitivity)
• Thereare3typesofhypersensitivity pneumonitis: acute, subacute, chronic
• InacuteHP,removalofincitingantigen results in resolution of symptoms within days.
*Lymphoplasmocytic interstitial infiltrate
with bronchiolocentric distribution on pathology
Epithelial injury (exact mechanism unknown)
*Organizing pneumonia
Dyspnea, tachypnea, and crackles
Abbreviations:
• HP – Hypersensitivity Pneumonitis
• PFT – Pulmonary Function Test
↑ Neutrophils, mast cells, macrophages, CD8+ T cells, & inflammatory cytokines
• *TriadofmainfindingsforsubacuteHP Systemic release of
cytokines disrupts hypothalamic regulation
Fever
Macrophages ingest antigens
*Poorly formed granulomas on pathology
Tissue breakdown from neutrophils activates fibroblasts, which deposit collagen
CT: Normal or diffuse ground- glass opacity (acute)
Chronic deposition of collagen replaces normal lung parenchyma by scar tissues (Chronic Findings)
Neutrophil elastase breaks down lung elastic fibers
Tissue destruction of alveolar walls creates larger air spaces
CT: Emphysema
CT: Honeycombing
(End stage Iung disease)
Pathology: Advanced interstitial fibrosis
PFT: Restrictive pattern ↓FEV1, ↓FVC, and ↓ DLCO
Legend:
Pathophysiology
Mechanism
Sign/Symptom/Lab Finding
Complications
Published September 1, 2016, updated October 5, 2021 on www.thecalgaryguide.com
Foundations
Systems
Other Languages
Respirology Other Causes of Dyspnea Hypersensitivity Pneumonitis: Pathogenesis and clinical findings Hypersensitivity-Pneumonitis