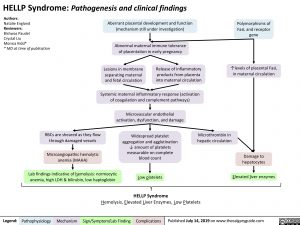
HELLP Syndrome: Pathogenesis and clinical findings
Authors:
Natalie England Reviewers:
Bishwas Paudel
Crystal Liu
Monica Kidd*
* MD at time of publication
Aberrant placental development and function (mechanism still under investigation)
Abnormal maternal immune tolerance of placentation in early pregnancy
Polymorphisms of FasL and receptor gene
↑levels of placental FasL in maternal circulation
Lesions in membrane separating maternal and fetal circulation
Release of inflammatory products from placenta into maternal circulation
Systemic maternal inflammatory response (activation of coagulation and complement pathways)
Microvascular endothelial activation, dysfunction, and damage
Widespread platelet aggregation and agglutination ↓ amount of platelets measurable on complete blood count
Low platelets
HELLP Syndrome
RBCs are sheared as they flow through damaged vessels
Microangiopathic hemolytic anemia (MAHA)
Lab findings indicative of hemolysis: normocytic anemia, high LDH & bilirubin, low haptoglobin
Microthrombin in hepatic circulation
Damage to hepatocytes
Elevated liver enzymes
Hemolysis, Elevated Liver Enzymes, Low Platelets
Legend:
Pathophysiology
Mechanism
Sign/Symptom/Lab Finding
Complications
Published July 14, 2019 on www.thecalgaryguide.com
Foundations
Systems
Other Languages
Obstetrics Pregnancy Complications HELLP Syndrome: Pathogenesis and clinical findings HELLP syndrome pathogenesis and clinical findings