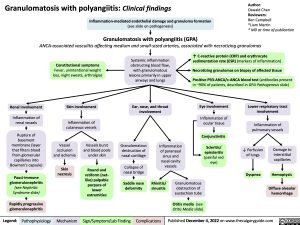
Granulomatosis with polyangiitis: Clinical findings Inflammation-mediated endothelial damage and granuloma formation
(see slide on pathogenesis)
Granulomatosis with polyangiitis (GPA)
Author:
Oswald Chen
Reviewers:
Ben Campbell
*Liam Martin
* MD at time of publication
ANCA-associated vasculitis affecting medium and small-sized arteries, associated with necrotizing granulomas
Constitutional symptoms
Fever, unintentional weight loss, night sweats, arthralgias
Skin involvement
Inflammation of cutaneous vessels
Systemic inflammation obstructing blood flow, with granulomatous lesions primarily in upper airways and lungs
Ear, nose, and throat involvement
↑ C-reactive protein (CRP) and erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR) (markers of inflammation)
Necrotizing granulomas on biopsy of affected tissue
Positive PR3-ANCA/c-ANCA blood test (antibodies present in ~90% of patients, described in GPA Pathogenesis slide)
Renal involvement
Inflammation of renal vessels
Rupture of basement membrane (layer that filters blood from glomerular capillaries into Bowman’s capsule)
Pauci-immune glomerulonephritis (see Nephritic Syndrome slide)
Rapidly progressive glomerulonephritis
Eye involvement
Inflammation of ocular tissue
Conjunctivitis
Scleritis/ episcleritis (painful red eye)
Lower respiratory tract involvement
Inflammation of pulmonary vessels
Vessel occlusion and ischemia
Skin necrosis
Vessels burst and blood pools under skin
Round and retiform (net- like) palpable purpura of lower extremities
Granulomatous destruction of nasal cartilage
Collapse of nasal bridge
Saddle nose deformity
Inflammation of paranasal sinus and nasal cavity vessels
↓ Perfusion of lungs
Dyspnea
Damage to interstitial capillaries
Hemoptysis
Diffuse alveolar hemorrhage
Rhinitis/ sinusitis
Granulomatous obstruction of eustachian tube
Otitis media (see Otitis Media slide)
Legend:
Pathophysiology
Mechanism
Sign/Symptom/Lab Finding
Complications
Published December 4, 2022 on www.thecalgaryguide.com