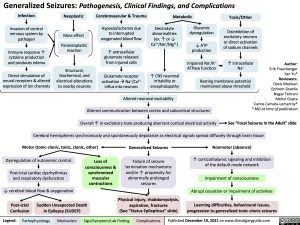
Generalized Seizures: Pathogenesis, Clinical Findings, and Complications
Infection
Invasion of central nervous system by pathogen
Immune response ↑ cytokine production and produces edema
Direct stimulation of neural receptors & altered expression of ion channels
Neoplastic
Mass effect
Paraneoplastic reaction
Structural, biochemical, and electrical alterations to nearby neurons
Cerebrovascular & Trauma
Hypoxia/ischemia due to interrupted oxygenated blood flow
↑ extracellular glutamate released from injured cells
Glutamate receptor activationàNa+/Ca2+ influx into neurons
Metabolic
Toxic/Other
Disinhibition of excitatory neurons or direct activation of sodium channels
↑ intracellular Na+
Electrolyte abnormalities (ex. ↑ or ↓ Ca2+/Na+/Mg2+)
↑ CNS neuronal irritability or encephalopathy
Glycemic dysregulation
↓ ATP production
Impaired Na+/K+ ATPase function
Author: Erik Fraunberger Yan Yu* Reviewers: Davis Maclean Ephrem Zewdie Negar Tehrani Mehul Gupta Carlos Camara-Lemarroy* * MD at time of publication
Overall ↑ in excitatory tone producing aberrant cortical electrical activity
Cerebral hemispheres synchronously and spontaneously depolarize as electrical signals spread diffusely through brain tissue
Resting membrane potential maintained above threshold
Altered neuronal excitability
Altered communication between cortex and subcortical structures
See “Focal Seizures in the Adult” slide
Motor (tonic-clonic, tonic, clonic, other)
Generalized Seizures
Failure of seizure termination mechanisms and/or ↑ propensity for abnormally prolonged seizures
Physical injury, rhabdomyolysis, aspiration, fractures
(See “Status Epilepticus” slide)
Nonmotor (absence)
↑ corticothalamic signaling and inhibition of the default mode network
Impairment of consciousness
Abrupt cessation or impairment of activities
Learning difficulties, behavioural issues, progression to generalized tonic-clonic seizures
Dysregulation of autonomic control
Post-ictal cardiac dysrhythmias and respiratory dysfunction
↓ cerebral blood flow & oxygenation
Post-ictal Sudden Unexpected Death Confusion In Epilepsy (SUDEP)
Loss of consciousness &
synchronized muscular contractions
Legend:
Pathophysiology
Mechanism
Sign/Symptom/Lab Finding
Complications
Published December 19, 2021 on www.thecalgaryguide.com
Foundations
Systems
Other Languages
Neurology Seizures Generalized Seizures: Pathogenesis, Clinical Findings, and Complications generalized-seizures-pathogenesis-clinical-findings-and-complications