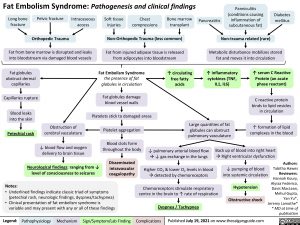
Fat Embolism Syndrome: Pathogenesis and clinical findings
Panniculitis (conditions causing
inflammation of subcutaneous fat)
Non-trauma related (rare)
Long bone fracture
Pelvic fracture
Orthopedic Trauma
Intraosseous access
Soft tissue injuries
Chest compressions
Bone marrow transplant
Pancreatitis
Diabetes mellitus
Fat from bone marrow is disrupted and leaks into bloodstream via damaged blood vessels
Fat globules obstruct dermal capillaries
Capillaries rupture
Blood leaks into the skin
Petechial rash
Non-Orthopedic Trauma (less common)
Fat from injured adipose tissue is released from adipocytes into bloodstream
Metabolic disturbance mobilizes stored fat and moves it into circulation
Fat Embolism Syndrome
the presence of fat globules in circulation
Fat globules damage blood vessel walls
Platelets stick to damaged areas Platelet aggregation
↑ circulating free fatty acids
↑ inflammatory cytokines (TNF, IL1, IL6)
↑ serum C Reactive Protein (an acute phase reactant)
C reactive protein binds to lipid vesicles in circulation
↑ formation of lipid complexes in the blood
Obstruction of cerebral vasculature
↓ blood flow and oxygen delivery to brain tissue
Neurological findings: ranging from ↓ level of consciousness to seizures
Notes:
Large quantities of fat globules can obstruct pulmonary vasculature
Blood clots form throughout the body
Disseminated intravascular coagulopathy
Back up of blood into right heart àRight ventricular dysfunction
↓ pulmonary arterial blood flow à↓ gas exchange in the lungs
Higher CO2 & lower O2 levels in blood àdetected by chemoreceptors
Chemoreceptors stimulate respiratory centre in the brain to ↑ rate of respiration
Dyspnea / Tachypnea
Authors: Tabitha Hawes Reviewers: Hannah Koury, Alyssa Federico, Davis MacLean, Mehul Gupta, Yan Yu*, Jeremy Lamothe* * MD at time of publication
• Underlined findings indicate classic triad of symptoms (petechial rash, neurologic findings, dyspnea/tachypnea)
• Clinical presentation of fat embolism syndrome is variable and may present with any or all of these findings
↓ pumping of blood into systemic circulation
Hypotension Obstructive shock
Legend:
Pathophysiology
Mechanism
Sign/Symptom/Lab Finding
Complications
Published July 19, 2021 on www.thecalgaryguide.com