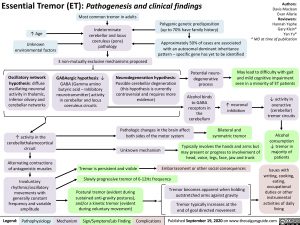
Essential Tremor (ET): Pathogenesis and clinical findings Most common tremor in adults
Authors: Davis Maclean Evan Allarie Reviewers: Hannah Yaphe Gary Klein* Yan Yu* * MD at time of publication
↑ Age
Unknown environmental factors
Oscillatory network hypothesis: diffuse
oscillating neuronal activity in thalamic, inferior olivary and cerebellar networks
↑ activity in the cerebellothalamocortical circuit
Alternating contractions of antagonistic muscles
Involuntary rhythmic/oscillatory
movements with generally constant frequency and variable amplitude
Indeterminate cerebellar and locus coeruleus (pons) pathology
3 non-mutually exclusive mechanisms proposed
Polygenic genetic predisposition (up to 70% have family history)
Approximately 50% of cases are associated with an autosomal dominant inheritance pattern – specific gene has yet to be identified
GABAergic hypothesis: ↓ GABA (Gamma amino
butyric acid – Inhibitory neurotransmitter) activity in cerebellar and locus coeruleus circuits
Neurodegeneration hypothesis: Possible cerebellar degeneration (this hypothesis is currently controversial and requires more evidence)
Potential neuro- degenerative process
May lead to difficulty with gait
and mild cognitive impairment seen in a minority of ET patients
Alcohol binds to GABA receptors in the cerebellum
↑ neuronal inhibition
Bilateral and symmetric tremor
↓ activity in overactive (cerebellar) tremor circuits
Alcohol consumption ↓ tremor in majority of patients
Issues with writing, cooking, eating, occupational duties or other instrumental activities of daily living
Pathologic changes in the brain affect both sides of the motor system
Unknown mechanism
Typically involves the hands and arms but may present or progress to involvement of head, voice, legs, face, jaw and trunk
Embarrassment or other social consequences Slowly progressive tremor of 6-12Hz frequency
Tremor is persistent and visible
Postural tremor (evident during sustained anti-gravity postures), and/or a kinetic tremor (evident during voluntary movement)
Tremor becomes apparent when holding outstretched arms against gravity
Tremor typically increases at the end of goal directed movement
Legend:
Pathophysiology
Mechanism
Sign/Symptom/Lab Finding
Complications
Published September 19, 2020 on www.thecalgaryguide.com