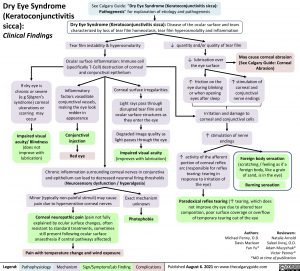
Dry Eye Syndrome (Keratoconjunctivitis
sicca):
Clinical Findings
If dry eye is chronic or severe (e.g Sjögren’s syndrome) corneal ulcerations or scarring may occur
Impaired visual acuity/ Blindness (does not improve with lubrication)
See Calgary Guide: “Dry Eye Syndrome (Keratoconjunctivitis sicca): Pathogenesis” for explanation of etiology and pathogenesis
Dry Eye Syndrome (Keratoconjunctivitis sicca): Disease of the ocular surface and tears characterized by loss of tear film homeostasis, tear film hyperosmolality and inflammation
Tear film instability & hyperosmolarity
Ocular surface inflammation: Immune cell (specifically T-Cell) destruction of corneal and conjunctival epithelium
↓ quantity and/or quality of tear film
Inflammatory factors vasodilate conjunctival vessels, making the eye look redder in appearance
Conjunctival injection
Red eye
Corneal surface irregularities
Light rays pass through
disrupted tear film and ocular surface structures as they enter the eye
Degraded image quality as light passes through the eye
Impaired visual acuity
(improves with lubrication)
↓ lubrication over the eye surface
↑ friction on the eye during blinking or when opening eyes after sleep
May cause corneal abrasion (See Calgary Guide: Corneal Abrasion)
↑ stimulation of corneal and conjunctival nerve endings
Irritation and damage to corneal and conjunctival cells
↑ stimulation of nerve endings
Chronic inflammation surrounding corneal nerves in conjunctiva and epithelium can lead to decreased neuronal firing thresholds (Neurosensory dysfunction / hyperalgesia)
↑ activity of the afferent portion of corneal reflex arc (responsible for reflex tearing: tearing in response to irritation of the eye)
Foreign body sensation
(scratching / feeling as if a foreign body, like a grain of sand, is in the eye)
Minor (typically non-painful stimuli) may cause pain due to hypersensitive corneal nerves
Corneal neuropathic pain (pain not fully explained by ocular surface changes, often resistant to standard treatments, sometimes still present following ocular surface anaesthesia if central pathways affected)
Pain with temperature change and wind exposure
Exact mechanism unknown
Photophobia
Burning sensation Paradoxical reflex tearing (↑ tearing, which does
not improve dry eye due to altered tear composition, poor surface coverage or overflow of temporary tearing out of the eye
Authors: Michael Penny, O.D. Davis Maclean Yan Yu*
Reviewers: Natalie Arnold Saleel Jivraj, O.D. Adam Muzychuk* Victor Penner* *MD at time of publication
Legend:
Pathophysiology
Mechanism
Sign/Symptom/Lab Finding
Complications
Published August 6. 2021 on www.thecalgaryguide.com
Foundations
Systems
Other Languages
Ophthalmology Non-Emergent Acute Vision Loss Dry Eye Syndrome: Clinical Findings Dry-Eye-Syndrome-Clinical-Findings