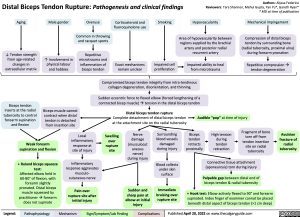
Distal Biceps Tendon Rupture: Pathogenesis and clinical findings
Authors: Alyssa Federico Reviewers: Tara Shannon, Mehul Gupta, Yan Yu*, Gareth Ryan* * MD at time of publication
Aging
↓ Tendon strength from age-related changes in extracellular matrix
Male gender
Overuse
Common in throwing and racquet sports
Repetitive microtrauma and inflammation of biceps tendon
Corticosteroid and fluoroquinolone use
Smoking
Hypovascularity
Area of hypovascularity between regions supplied by the brachial artery and posterior radial recurrent artery
Impaired ability to heal from microtrauma
Mechanical impingement
Compression of distal biceps
tendon by surrounding bone (radial tuberosity, proximal ulna) during forearm pronation
Repetitive compressionà tendon degeneration
↑ Involvement in physical labour and hobbies
Exact mechanisms remain unclear
Impaired cell proliferation
Biceps tendon inserts at the radial tuberosity to control forearm supination and flexion
Compromised biceps tendon integrity from intra-tendinous collagen degeneration, disorientation, and thinning
Sudden eccentric force to flexed elbow (forced lengthening of a contracted bicep muscle)àtension in the distal biceps tendon
Biceps muscle cannot contract when distal tendon is detached from insertion site
Distal biceps tendon rupture
Complete detachment of distal biceps tendon at the attachment site on the radial tuberosity
Audible “pop” at time of injury
Weak forearm supination and flexion
+ Ruland biceps squeeze test:
Affected elbow held in 60-80° of flexion, with forearm slightly pronated. Distal biceps muscle squeezed by practitioner à forearm does not supinate
Local inflammatory response at site of injury
Inflammatory response aggravates musculo- cutaneous nerve
Pain over rupture site after initial injury
Swelling over rupture site
Nerve damage (musculocut aneous nerve) during injury
Sudden and sharp pain at
elbow at initial injury
Surrounding blood vessels damaged during injury
Blood collects under skin surface
Immediate bruising over rupture site
Biceps tendon retracts proximally
High tension during tendon retraction
Fragment of bone torn off from tendon insertion site on radial tuberosity
Avulsion fracture of
radial tuberosity
Connective tissue attachment (aponeurosis) torn during injury
Palpable gap between distal end of biceps tendon & radial tuberosity
+ Hook test: Elbow actively flexed to 90° and forearm supinated. Index finger of examiner cannot be placed beneath distal aspect of biceps tendon (>1 cm deep)
Legend:
Pathophysiology
Mechanism
Sign/Symptom/Lab Finding
Complications
Published April 20, 2022 on www.thecalgaryguide.com