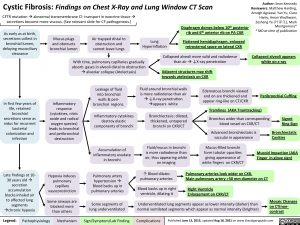
Cystic Fibrosis: Findings on Chest X-Ray and Lung Window CT Scan CFTR mutationàabnormal transmembrane Cl- transport in exocrine tissueà
Author: Sean Kennedy Reviewers: Matthew Harding, Amogh Agrawal, Yan Yu, Ciara
Hanly, Aman Wadhwani, Zesheng Ye (), Mark Montgomery* * MD at time of publication
Collapsed alveoli appears white on x-ray
Peribronchial Cuffing
secretions become more viscous. (See relevant slide for CF pathogenesis.)
As early as at birth, secretions collect in bronchial lumen, delaying mucociliary clearance
Mucus plugs and obstructs bronchial lumen
Air trapped distal to obstruction and cannot leave lungs
Lung Hyperinflation
Diaphragm domes below 10th posterior rib and 6th anterior rib on PA CXR
Flattened hemidiaphragm, enlarged retrosternal space on lateral CXR
With time, pulmonary capillaries gradually absorb gases in alveoli distal to obstruction àalveolar collapse (Atelectasis)
Collapsed alveoli more solid and radiodense than airà↓X-ray penetration
Adjacent structures may shift towards atelectasis on CXR
In first few years of life, retained bronchial secretions serve as nidus for recurrent bacterial colonization and infection
Late findings at 10- 30 years oldà secretion accumulation blocks inhaled air to affected lung segments àchronic hypoxia
Inflammatory response (cytokines, nitric oxide and radical oxygen species) leads to bronchial and peribronchial destruction
Hypoxia induces pulmonary capillary vasoconstriction
Some airways are blocked more than others
Leakage of fluid into bronchial walls & peri- bronchial regions.
Inflammatory cytokines destroy elastic components of bronchi
Accumulation of inflammatory exudate in bronchi
Pulmonary artery hypertension à Blood backs up in pulmonary arteries
Some segments of lung underventilated
Fluid around bronchial walls is more radiodense than air à↓X-ray penetration àappears white
Bronchiectasis: dilated, thickened, untapered bronchi on CXR/CT
Fluid/mucus in bronchi is more radiodense than air, thus appearing white on imaging
Edematous bronchi viewed end on are thickened and appear ring-like on CT/CXR
Tramlines (AKA Tramtracking)
Bronchus wider than corresponding blood vessel on CXR/CT
Advanced bronchiectasis is saccular in appearance
Mucus-filled bronchi form tubular opacities giving appearance of white fingers on CXR/CT
Signet Ring Sign
Bronchiectatic Cavities
Mucoid Impaction (AKA Finger in glove sign)
↑ Blood dilates pulmonary arteries
Blood backs up in right ventricle, dilating it
Pulmonary arteries look wider on CXR.
Main pulmonary artery >30 mm diameter on CT
Right Ventricle Enlargement on CXR/CT
Underventilated lung segments appear as lower intensity (darker) than normal ventilated segments which appear as normal intensity (brighter)
Mosaic Changes on CT(non- contrast
Legend:
Pathophysiology
Mechanism
Sign/Symptom/Lab Finding
Complications
Published June 13, 2013, updated Aug 18, 2021 on www.thecalgaryguide.com
Foundations
Systems
Other Languages
Radiology Body Radiology Cystic Fibrosis: Findings on Chest X-Ray and Lung Window CT Scan cystic-fibrosis-findings-on-chest-x-ray-and-lung-window-ct-scan