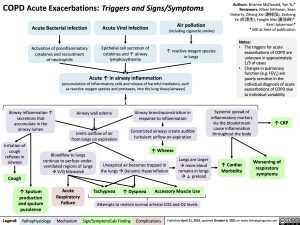
COPD Acute Exacerbations: Triggers and Signs/Symptoms
Authors: Brianne McDonald, Yan Yu* Reviewers: Nilani Sritharan, Sean Doherty, Zihong Xie (谢梓泓), Zesheng Ye (叶泽生), Yonglin Mai (麦泳琳)*, Kerri Johannson* * MD at time of publication
Notes:
• The triggers for acute exacerbations of COPD are unknown in approximately 1/3 of cases
• Changes in pulmonary function (e.g. FEV1) are poorly sensitive in the individual diagnosis of acute exacerbations of COPD due to individual variability
Acute Bacterial Infection
Activation of proinflammatory cytokines and recruitment of neutrophils
Acute Viral Infection
Epithelial cell secretion of cytokines and ↑ airway lymphocythemia
Acute ↑ in airway inflammation
(accumulation of inflammatory cells and release of harmful mediators, such as reactive oxygen species and proteases, into the lung tissue/airways)
Air pollution
(including cigarette smoke)
↑ reactive oxygen species in lungs
Airway inflammation ↑ secretions that accumulate in the airway lumen
Airway wall edema
Limits outflow of air from lungs on expiration
Airway bronchoconstriction in response to inflammation
Constricted airways create audible turbulent airflow on expiration
Systemic spread of inflammatory markers via the bloodstream cause inflammation throughout the body
↑ Cardiac Morbidity
↑ CRP
Worsening of respiratory symptoms
Irritation of cough reflexes in airways
Cough
↑ Sputum production and sputum purulence
↑ Wheeze Unexpired air becomes trapped in
the lungsàDynamic Hyperinflation
Bloodflow to lungs continue to perfuse under- ventilated regions of lungs àV/Q Mismatch
Lungs are larger àmore blood
remains in lungs à↓ preload
Acute Respiratory Failure
Tachypnea
↑ Dyspnea
Accessory Muscle Use
Attempts to restore normal arterial CO2 and O2 levels
Legend:
Pathophysiology
Mechanism
Sign/Symptom/Lab Finding
Complications
Published April 21, 2019, updated October 6, 2021 on www.thecalgaryguide.com
Foundations
Systems
Other Languages
Respirology Obstructive Lung Disease COPD Acute Exacerbations: Triggers and Signs/Symptoms COPD Acute Exacerbations