Pathogenesis of Select Causes of Constipation in Adults and in Elderly
Authors: Reviewers: Lina Cadili Peter Bishay Joseph Tropiano Kirles Bishay* *MD at time of publication
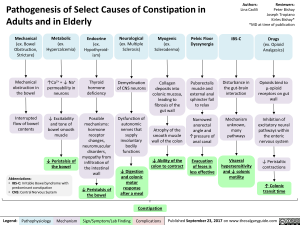
Mechanical Metabolic Endocrine Neurological Myogenic Pelvic Floor IBS-C Drugs (ex. Bowel (ex. (ex. (ex. Multiple (ex. Dyssynergia (ex. Opioid Obstruction, Stricture) Hypercalcemia) Hypothyroid-ism) Sclerosis) Scleroderma) Analgesics)
Mechanical I`Ca2+ = 4, Na+ Thyroid Demyelination Collagen Puborectalis Disturbance in obstruction in permeability in hormone of CNS neurons deposits into muscle and the gut-brain the bowel neurons deficiency colonic mucosa, leading to external anal sphincter fail interaction fibrosis of the gut wall to relax Interrupted 4, Excitability Possible Dysfunction of Narrowed Mechanism flow of bowel contents and tone of bowel smooth mechanisms: hormone autonomic nerves that anorectal angle and unknown, many Atrophy of the muscle receptor supply smooth muscle ‘`pressure of pathways changes, involuntary wall of the colon anal canal neuromuscular disorders, myopathy from bodily functions 1, Peristalsis of infiltration of 4, Ability of the Evacuation Visceral the bowel colon to contract of feces is hypersensitivity Abbreviations: the intestinal wall 4, Digestion less effective and 4, colonic and colonic motility motor • IBS-C: Irritable Bowel Syndrome with predominant constipation • CNS: Central Nervous System 4, Peristalsis of response after a meal the bowel
Opioids bind to Lt-opioid receptors on gut wall
Inhibition of excitatory neural pathways within the enteric nervous system
1, Peristaltic contractions
1
l• Colonic transit time
Foundations
Systems
Other Languages
pathogenesis-of-select-causes-of-constipation-in-adults-and-in-elderly