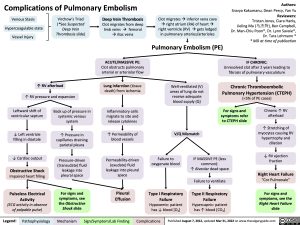
Complications of Pulmonary Embolism
Authors:
Sravya Kakumanu, Dean Percy, Yan Yu
Reviewers:
Tristan Jones, Ciara Hanly, Jieling Ma (马杰羚), Ben Campbell, Dr. Man-Chiu Poon*, Dr. Lynn Savoie*, Dr. Tara Lohmann * * MD at time of publication
IF CHRONIC:
Unresolved clot after 2 years leading to fibrosis of pulmonary vasculature
Chronic Thromboembolic Pulmonary Hypertension (CTEPH)
(<5% of PE cases)
Venous Stasis Hypercoagulable state
Vessel Injury
Virchow’s Triad (*See Suspected Deep Vein Thrombosis slide)
Deep Vein Thrombosis
Clot migrates from deep limb veins à femoral àiliac veins
ACUTE/MASSIVE PE:
Clot obstructs pulmonary arterial or arteriolar flow
Lung infarction (tissue death) from ischemia
Inflammatory cells migrate to site and release cytokines
↑ Permeability of blood vessels
Permeability-driven (exudate) fluid leakage into pleural space
Pleural Effusion
Clot migratesàinferior vena cava àright atrium (RA) of heartà right ventricle (RV) à gets lodged in pulmonary arteries/arterioles
Pulmonary Embolism (PE)
↑ RV afterload
↑ RV pressure and expansion
Well-ventilated (V) areas of lung do not receive adequate blood supply (Q)
V/Q Mismatch
Leftward shift of ventricular septum
↓ Left ventricle filling in diastole
↓ Cardiac output
Obstructive Shock
Impaired heart filling
Pulseless Electrical Activity
(ECG activity in absence of palpable pulse)
Back up of pressure in systemic venous system
↑ Pressure in capillaries draining parietal pleura
Pressure-driven (transudate) fluid leakage into pleural space
For signs and symptoms, see the Obstructive Shock slide
For signs and symptoms refer to CTEPH slide
Chronic ↑ RV afterload
↑ Stretching of myocytes causing RV hypertrophy and dilation
↓ RV ejection fraction
Right Heart Failure
“Cor Pulmonale”
For signs and symptoms, see the Right Heart Failure slide
Failure to oxygenate blood
Type I Respiratory Failure
Hypoxemic: patient has ↓ blood [O2]
IF MASSIVE PE (less common):
↑ Alveolar dead space
Failure to ventilate
Type II Respiratory Failure Hypercapnic: patient has ↑ blood [CO2]
Legend:
Pathophysiology
Mechanism
Sign/Symptom/Lab Finding
Complications
Published August 7, 2012, updated Mar 31, 2022 on www.thecalgaryguide.com
Foundations
Systems
Other Languages
Respirology Lung Vascular Disorders Complications of Pulmonary Embolism complications-of-pulmonary-embolism