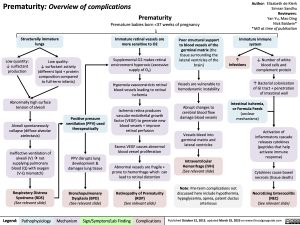
Prematurity: Overview of complications
Premature babies born <37 weeks of pregnancy
Author: Elizabeth de Klerk Simran Sandhu Reviewers: Yan Yu, Mao Ding Nick Baldwin* *MD at time of publication
Immature immune system
Prematurity
Structurally immature lungs
Immature retinal vessels are more sensitive to O2
Supplemental O2 makes retinal environment hyperoxic (excessive supply of O2)
Hyperoxia vasoconstricts retinal blood vessels leading to retinal ischemia
Ischemic retina produces vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) to generate new blood vessels + improve retinal perfusion
Excess VEGF causes abnormal blood vessel proliferation
Abnormal vessels are fragile + prone to hemorrhage which can lead to retinal distortion
Retinopathy of Prematurity (ROP)
(See relevant slide)
Poor structural support to blood vessels of the germinal matrix (the tissue surrounding the lateral ventricles of the brain)
Vessels are vulnerable to hemodynamic instability
Abrupt changes to cerebral blood flow damage blood vessels
Vessels bleed into germinal matrix and lateral ventricles
Intraventricular Hemorrhage (IVH) (See relevant slide)
Note: Pre-term complications not discussed here include hypothermia, hypoglycemia, apnea, patent ductus arteriosus
Low quantity: ↓ surfactant production
Low quality:
↓ surfactant activity (different lipid + protein composition compared to full-term infants)
↑
Infections
↓ Number of white blood cells and complement protein
↑ Bacterial colonization of GI tract + penetration of intestinal wall
Abnormally high surface tension of alveoli
Alveoli spontaneously collapse (diffuse alveolar atelectasis)
Ineffective ventilation of alveoli (V)ànot supplying pulmonary blood (Q) with oxygen (V-Q mismatch)
Respiratory Distress Syndrome (RDS) (See relevant slide)
Positive pressure ventilation (PPV) used therapeutically
PPV disrupts lung development & damages lung tissue
Bronchopulmonary Dysplasia (BPD) (See relevant slide)
Intestinal ischemia, or Formula Feeds (unclear mechanisms)
Activation of inflammatory cascade releases cytokines (peptides that help activate immune response)
Cytokines cause bowel necrosis (tissue death)
Necrotizing Enterocolitis (NEC)
(See relevant slide)
Legend:
Pathophysiology
Mechanism
Sign/Symptom/Lab Finding
Complications
Published October 31, 2013, updated March 25, 2023 on www.thecalgaryguide.com
Foundations
Systems
Other Languages
Pediatrics Complications of Pre-Term Infancy Complications of Prematurity – Overview Complications of Prematurity