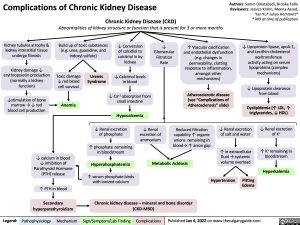
Complications of Chronic Kidney Disease Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD)
Authors: Samin Dolatabadi, Brooke Fallis Reviewers: Jessica Krahn, Meena Assad, Yan Yu* Juliya Hemmett* * MD at time of publication
Abnormalities of kidney structure or function that is present for 3 or more months
Kidney tubules atrophy & kidney interstitial tissue undergo fibrosis
Kidney damage ↓ erythropoietin production (normally a kidney function)
↓stimulation of bone marrow → ↓ red blood cell production
Build up of toxic substances (e.g. urea, guanidine, and indoxyl sulfate)
↓ Conversion of calcidiol to calcitriol in by kidney
↓ Calcitriol levels in blood
↓ Ca+2 absorption from small intestine
Hypocalcemia
↓ Glomerular Filtration Rate
↑ Vascular calcification and endothelial dysfunction (e.g. changes in permeability, clotting response to inflammation, amongst other mechanisms)
Atherosclerotic disease (see “Complications of Atherosclerosis” slide)
↓ Lipoprotein lipase, apoA-1, and Lecithin-cholesterol acyltransferase
activity acting on serum lipoproteins (complex mechanisms)
↓ Lipoprotein clearance from blood
Dyslipidemia (↑ LDL, ↑ triglycerides, ↓ HDL)
Toxic damage ↓ red blood cell survival
Anemia
Uremic Syndrome
↓ Renal excretion of phosphate
↑ phosphate remaining in bloodstream
Hyperphosphatemia
↑ serum phosphate binds with ionized calcium
↓ Renal excretion of K+
↑ K+ remaining in bloodstream
Hyperkalemia Edema
↓ Renal excretion of ammonium
Reduced filtration capability ↑ organic anions remaining in blood→ ↑ anion gap
↓ Renal excretion of salt and water
↑ in extracellular fluid → systemic volume overload
↓ calcium in blood ↓ inhibition of Parathyroid Hormone (PTH) release
↑ PTH in blood
Secondary hyperparathyroidism
Metabolic Acidosis
Hypertension
Pitting
Chronic kidney disease – mineral and bone disorder (CKD-MBD)
Legend:
Pathophysiology
Mechanism
Sign/Symptom/Lab Finding
Complications
Published Jan 4, 2022 on www.thecalgaryguide.com
Foundations
Systems
Other Languages
Nephrology Kidney Injury Complications of Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD) complications-of-chronic-kidney-disease-ckd