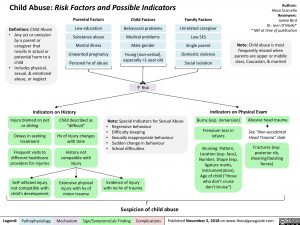
Child Abuse: Risk Factors and Possible Indicators
Authors: Alexa Scarcello Reviewers: Jaimie Bird Dr. Jenn D’Mello* * MD at time of publication
Note: Child abuse is most frequently missed when parents are upper or middle class, Caucasian, & married
Parental Factors
Low education
Substance abuse Mental illness Unwanted pregnancy Personal hx of abuse
Child Factors
Behavioral problems
Medical problems
Male gender
Young (non-verbal), especially <1 year old
↑ Risk
Note: Special Indicators for Sexual Abuse
Definition: Child Abuse
• Any act or omission
by a parent or caregiver that results in actual or potential harm to a child
• Includes physical, sexual, & emotional abuse, or neglect
Family Factors
Unrelated caregiver Low SES Single parent Domestic violence Social isolation
Indicators on History
Indicators on Physical Exam
Injury blamed on pet or sibling
Delays in seeking treatment
Frequent visits to different healthcare providers for injuries
Self-inflicted injury not compatible with child’s development
Child described as “difficult”
Hx of injury changes with time
History not compatible with injury
Extensive physical injury with hx of minor trauma
• • • • •
Regressive behaviour
Difficulty sleeping
Sexually inappropriate behaviour Sudden change in behaviour School difficulties
Burns (esp. immersion)
Frenulum tear in infants
Bruising: Pattern, Location (esp. face), Number, Shape (esp. ligature marks, instrumentation), Age of child (“those who don’t cruise don’t bruise”)
Abusive head trauma
See “Non-accidental Head Trauma” slide
Fractures (esp. posterior rib, shearing/twisting forces)
Evidence of injury with no hx of trauma
Suspicion of child abuse
Legend:
Pathophysiology
Mechanism
Sign/Symptom/Lab Finding
Complications
Published November 5, 2018 on www.thecalgaryguide.com
Foundations
Systems
Other Languages
Pediatrics Child Abuse Child Abuse: Risk Factors and Possible Indicators Child Abuse: Risk Factors and Possible Indicators