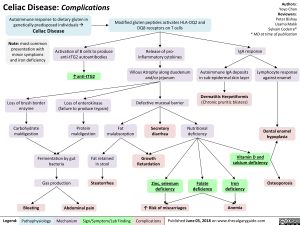
Celiac Disease: Complications
Autoimmune response to dietary gluten in genetically predisposed individuals 4 Celiac Disease
Note: most common presentation with minor symptoms and iron deficiency
Modified gluten peptides activates HLA-DQ2 and DQ8 receptors on T cells
Activation of B cells to produce anti-tTG2 autoantibodies
1
tanti-tTG2
Release of pro-inflammatory cytokines
Villous Atrophy along duodenum and/or jejunum
Loss of brush border Loss of enterokinase Defective mucosal barrier enzyme (failure to produce trypsin) Carbohydrate Protein Fat Secretory maldigestion maldigestion malabsorption diarrhea
Legend:
Fermentation by gut bacteria 1 Gas production
Bloating
Fat retained in stool
Steatorrhea
Abdominal pain
Pathophysiology Mechanism
Sign/Symptom/Lab Finding
Growth Retardation
Authors: Yoyo Chan Reviewers: Peter Bishay Usama Malik Sylvain Coderre* * MD at time of publication
IgA response
Autoimmune IgA deposits Lymphocyte response in sub-epidermal skin layer against enamel
Dermatitis Herpetiformis (Chronic pruritic blisters)
Nutritional deficiency
Dental enamel hypoplasia
Vitamin D and calcium deficiency
Zinc, selenium Folate Iron Osteoporosis deficiency deficiency deficiency Anemia t Risk of miscarriages