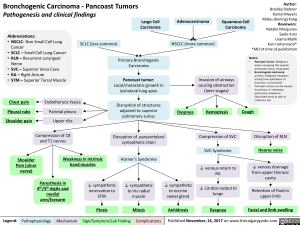
Bronchogenic Carcinoma – Pancoast Tumors
Pathogenesis and clinical findings
Abbreviations:
• NSCLC- Non Small Cell Lung
Cancer
• SCLC — Small Cell Lung Cancer
• RLN — Recurrent Laryngeal
Nerve
• SVC — Superior Vena Cava
• RA — Right Atrium
• STM — Superior Tarsal Muscle
Chest pain
Pleural rubs
Shoulder pain
SCLC (less common)
Endothoracic fascia
1— Parietal pleura •
1—
Upper ribs
Large Cell
Carcinoma
Adenocarcinoma
Squamous Cell
Carcinoma
Primary Bronchogenic
Carcinoma
Pancoast tumor:
Local/metastatic growth in
ipsilateral lung apex
Disruption of structures
adjacent to superior
pulmonary sulcus
NSCLC (more common)
Invasion of airways
► causing obstruction
(later stages)
Author:
Bradley Stebner
Daniel Meyers
Midas (Kening) Kang
Reviewers:
Natalie Morgunov
Sadie Kutz
Usama Malik
Kerri Johannson*
*MD at time of publication
Notes:
• Pancoast Tumor: Malignant
lesion occupying the superior
pulmonary sulcus (lung apex)
Bronchogenic carcinoma:
primary malignant neoplasm
arising from epithelium of
bronchus or bronchiole
Pancoast tumors can be caused
by primary or metastatic
pulmonary neoplasms
(described here) as well as
infectious foci
Hemoptysis
Compression of C8
and T1 nerves
•
Disruption of paravertebral
sympathetic chain
Shoulder • Weakness in intrinsic Horner’s • 4, sympathetic to to iris muscle Syndrome 4, sympathetic radial to eccrine sweat gland
Pain (ulnar hand muscles
nerve) 4, sympathetic innervation STM
Paresthesia in
4th /5th digits and
arm/forearm medial
Ptosis Mi o sis Anhidrosis Legend: Pathophysiology Mechanism
Sign/Symptom/Lab Finding
Compression of SVC
SVC Syndrome
•
4, venous return to
RA
4, Cardiac output to
lungs
Dyspnea
Disruption of RLN
1
Hoarse voice
4, venous drainage
from upper thoracic
cavity
Retention of fluid in
upper limb
•)r
Facial and limb swelling
Foundations
Systems
Other Languages
Respirology Pulmonary Neoplasms Bronchogenic Carcinoma – Pancoast Tumors Pathogenesis and Clinical Findings Bronchogenic Carcinoma – Pancoast Tumors Pathogenesis and clinical findings