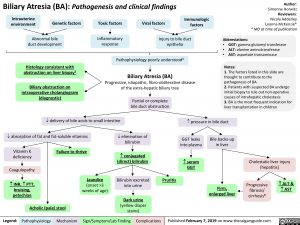
Biliary Atresia (BA)- Pathogenesis and clinical findings Intrauterine environment genetic factors abnormal bile duct development toxic inflammatory response viral immunologic injury to bile duct epithelia pathophysiology poorly understood histology consistent with obstruction on liver biopsy biliary atresia progressive idiopathic fibre-obliterative disease extra-hepatic biliary tree biliary obstruction on intra-operative cholangiogram (diagnostic) partial complete bile duct obstruction delivery of bile acids to small intestine pressure in bile duct absorption of fat and soluble vitamins vitamin K+ deficiency coagulopathy INR PTT bruising petechiae acholic pale stool failure to thrive elimination of bilirubin conjugated direct bilirubin jaundice pruritus excreted urine dark urine diaper yellow pressure bile duct GGT backs up in liver cholestatic hepatitis firm enlarged liver fibrosis cirrhosis ALT AST Horwitz Adderley McKenzie
Foundations
Systems
Other Languages
Pediatrics Other Pediatrics Biliary Atresia (BA): Pathogenesis and clinical findings Biliary Atresia (BA)- Pathogenesis and clinical findings