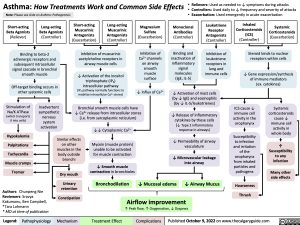
Asthma: How Treatments Work and Common Side Effects • Relievers: Used as needed to ↓ symptoms during attacks
• Controllers: Used daily to ↓ frequency and severity of attacks
Note: Please see slide on Asthma: Pathogenesis
• Exacerbation: Used emergently in acute exacerbation
Short-acting Beta Agonists (Reliever)
Long-acting Beta Agonists (Controller)
Short-acting Muscarinic Antagonists (Exacerbation)
Long-acting Muscarinic Antagonists (Controller)
Magnesium Sulfate (Exacerbation)
Monoclonal Antibodies (Controller)
Leukotriene Receptor Antagonists (Controller)
Inhaled Corticosteroids (ICS) (Controller)
Systemic Corticosteroids (Exacerbation)
Binding to beta-2 adrenergic receptors and subsequent intracellular signal cascade in bronchial smooth muscle
Off-target binding occurs in other systemic cells
Inhibition of muscarinic acetylcholine receptors in airway muscle cells
↓ Activation of the inositol triphosphate (IP3)
intracellular pathway
(IP3 pathway normally functions to mobilize intracellular Ca2+ stores)
Inhibition of Ca2+ channels on airway smooth muscle surface
↓ Influx of Ca2+
Binding and inactivation of inflammatory signal molecules (IgE, IL-5)
Inhibition of leukotriene receptors in lung and immune cells
Steroid binds to nuclear receptors within cells
↓ Gene expression/synthesis of immune mediators (ex. cytokines)
Stimulation of
Na/K ATPase (which transports K into cells)
Hypokalemia Palpitations Tachycardia Muscle cramps Tremor
Authors: Chunpeng Nie Reviewers: Sravya Kakumanu, Ben Campbell, *Tara Lohmann
* MD at time of publication
↓ Activation of mast cells (by ↓ IgE) and eosinophils (by ↓ IL-5/leukotrienes)
↓ Release of inflammatory cytokines by these cells (↓ Type 2 inflammatory response in airways)
↓ Permeability of airway vasculature
↓ Microvascular leakage into airway
Inadvertent sympathetic nervous system activation
Bronchial smooth muscle cells have ↓ Ca2+ release from intracellular stores (i.e. from sarcoplasmic reticulum)
↓↓ Cytoplasmic Ca2+
Myosin (muscle protein) unable to be activated for muscle contraction
↓ Smooth muscle contraction in bronchioles
Bronchodilation
ICS cause ↓
immune cell activity in the oropharynx
Susceptibility to infection and irritation of the oropharynx from inhaled particles and pathogens
Hoarseness Thrush
Systemic corticosteroids cause ↓ immune cell activity in whole body
↑ Susceptibility to any infection
Many other side effects
Similar effects on other muscles in the body outside bronchi
Dry mouth
Urinary retention
Constipation
↓ Mucosal edema
↓ Airway Mucus
Airflow improvement
↑ Peak flow, ↑ Oxygenation, ↓ Dyspnea
Legend:
Pathophysiology
Mechanism
Treatment Effect
Complications
Published October 9, 2022 on www.thecalgaryguide.com
Foundations
Systems
Other Languages
Respirology Obstructive Lung Disease Asthma: How Treatments Work and Common Side Effects asthma-how-treatments-work-and-common-side-effects