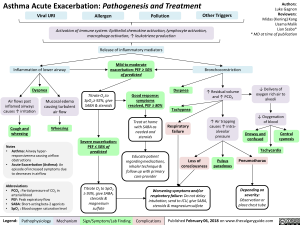
Asthma Acute Exacerbation: Pathogenesis and Treatment
Viral URI
Allergen
Pollution
Other Triggers
Activation of immune system: Epithelial chemokine activation, lymphocyte activation, macrophage activation, t leukotriene production
Inflammation of lower airway
• Dyspnea
Air flows past inflamed airways causes t irritation
Cough and wheezing
Release of inflammatory mediators
Mucosal edema causing turbulent air flow 7Ir Wheezing
Notes • Asthma: Airway hyper-responsiveness causing airflow obstructions • Acute Exacerbation (Asthma): An episode of increased symptoms due to decreases in airflow
Abbreviations • PCO2: Partial pressure of CO, in arterial blood • PEF: Peak expiratory flow • SABA: Short-acting beta-2 agonists • Sp02 : Blood oxygen saturation level
Mild to moderate exacerbation: PEF 50% of predicted
Titrate O2 toSpO2, 92%, give SABA & steroids ■
Good response: symptoms resolved, PEF > 80%
[Treat at home with SABA as needed and steroids
Dyspnea
Bronchoconstriction
1` Residual volume and 1` PCO2
Respiratory failure
1` Air trapping causes ‘1’ intra-alveolar pressure
Severe exacerbation: PEF 50% of predicted Educate patient regarding medications, Loss of Pulsus inhaler technique & [consciousness paradoxus follow up with primary care provider I
Legend: Pathophysiology Mechanism
Titrate O2 to402 93%, give SABA, steroids & magnesium sulfate
Sign/Symptom/Lab Finding
{Worsening symptoms and/or respiratory failure: Do not delay intubation, send to ICU, give SABA, steroids & magnesium sulfate
Authors: Luke Gagnon Reviewers: Midas (Kening) Kang Usama Malik Lian Szabo* * MD at time of publication
4, Delivery of oxygen rich air to alveoli 4, Oxygenation of blood
Drowsy and confused
Central cyanosis
• Tachycardia
Pneumothorax
[Depending on 1 severity: Observation or place chest tube