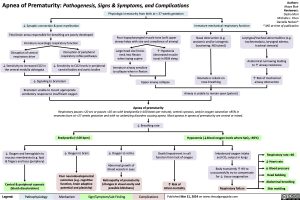
Apnea of Prematurity: Pathogenesis, Signs & Symptoms, and Complications Physiologic immaturity from birth at < 37 weeks gestation
Authors: Akaya Blair Reviewers:
Dasha Mori Michelle J. Chen Danielle Nelson* * MD at time of publication
↓ Synaptic connection & poor myelination
Fetal brain areas responsible for breathing are poorly developed Immature neurologic respiratory function
Immature mechanical respiratory function
Poor hypopharyngeal muscle tone (soft upper airway helps with size and compliance of airway)
Nasal obstruction (e.g. anatomic and/or iatrogenic [suctioning, NG tubes])
Neonate is reliant on nose breathing
Airway is unable to remain open (patent)
Laryngeal/tracheal abnormalities (e.g. tracheomalacia, laryngeal edema, tracheal stenosis)
Anatomical narrowing leading to ↑ airway resistance
↑ Risk of mechanical airway obstruction
Disruption of central respiratory drive
↓ Sensitivity to increased CO2 in the ventral medulla oblongata
Disruption of peripheral respiratory reflex pathways
↓ Sensitivity to CO2 levels in peripheral carotid bodies and aortic bodies
Large head size forces neck into flexion when laying supine
Immature airway sensitive to collapse when in flexion
↑ Hypotonia (decreased muscle tone) in REM sleep
↓ Signaling to brainstem
Brainstem unable to mount appropriate ventilatory response to insufficient oxygen
Upper airway collapse
Apnea of prematurity
Respiratory pauses >20 sec or pauses <20 sec with bradycardia (<100 beats per minute), central cyanosis, and/or oxygen saturation <85% in neonates born at <37 weeks gestation and with no underlying disorders causing apnea. Most apneas in apnea of prematurity are central or mixed.
↓ Breathing rate
Bradycardia (<100 bpm)
↓ Oxygen to brain
Poor neurodevelopmental outcomes (e.g. cognitive function, brain adaptive potential and plasticity)
Hypoxemia (↓blood oxygen levels where SpO2 <85%)
↓ Oxygen and hemoglobin to mucous membranes (e.g. lips) & fingers and toes (periphery)
Central & peripheral cyanosis (bluish discoloration)
↓ Oxygen to retina
Abnormal growth of blood vessels in eyes
Retinopathy of prematurity (changes in visual acuity and possible blindness)
Death/impairment in cell function from lack of oxygen
↑ Risk of infant mortality
Imbalanced oxygen intake and CO2 output in lungs
Body transiently ↑ HR to unsuccessfully try to compensate for ↓ tissue oxygenation
Respiratory failure
Respiratory rate >60 ↓ Heart rate
↓ Blood pressure
Head bobbing Abdominal breathing
Skin mottling
Legend:
Pathophysiology
Mechanism
Sign/Symptom/Lab Finding
Complications
Published Mar 21, 2024 on www.thecalgaryguide.com