Side effects
Authors: Arsalan Ahmad, Lance Bartel,
Yan Yu*
Reviewers: Billy Sun, Mackenzie Gault,
Melinda Davis*
*MD at time of publication
Legend: Published February 19, 2019 on www.Pathophysiology Mechanism Sign/Symptom/Lab Finding thecalgaryguide.com
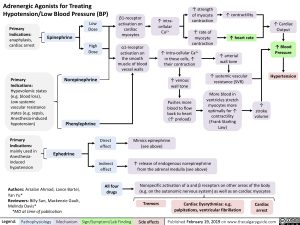
Epinephrine
Norepinephrine
High
Dose
Low
Dose
Adrenergic Agonists for Treating
Hypotension/Low Blood Pressure (BP) β1-receptor
activation on
cardiac
myocytes
↑ contractility
α1-receptor
activation on
the smooth
muscle of blood
vessel walls
↑ intra-cellular Ca2+
in these cells, ↑
their contraction
Ephedrine
Direct
effect
Indirect
effect
↑ release of endogenous norepinephrine
from the adrenal medulla (see above)
Mimics epinephrine
(see above)
Primary
Indications:
anaphylaxis,
cardiac arrest
Primary
Indications:
Hypovolemic states
(e.g. blood loss),
Low systemic
vascular resistance
states (e.g. sepsis,
Anesthesia-induced
hypotension)
Primary
Indications:
mainly used in
Anesthesiainduced
hypotension
↑ intracellular
Ca2+ ↑ rate of
myocyte
contraction
Phenylephrine
↑ Cardiac
Output
↑ heart rate
↑ strength
of myocyte
contraction
↑ arterial
wall tone
↑
stroke
volume
Pushes more
blood to flow
back to heart
(↑ preload)
↑ systemic vascular
resistance (SVR)
More blood in
ventricles stretch
myocytes more
optimally for ↑
contractility
(Frank Starling
Law)
↑ venous
wall tone
↑ Blood
Pressure
Nonspecific activation of α and β receptors on other areas of the body
(e.g. on the autonomic nervous system) as well as on cardiac myocytes
Hypertension
Cardiac Dysrythmias: e.g.
palpitations, ventricular fibrillation
Tremors Cardiac
arrest
All four
drugs
Foundations
Systems
Other Languages
Pharmacology Cardiovascular Adrenergic Agonists for Treating Hypotension/Low Blood Pressure adrenergic-agonists-for-treating-hypotensionlow-blood-pressure