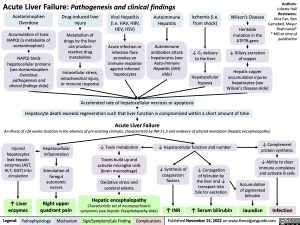
Acute Liver Failure: Pathogenesis and clinical findings
Authors: Juliette Hall Reviewers: Vina Fan, Ben Campbell, Mayur Brahmania* * MD at time of publication
Acetaminophen Overdose
Accumulation of toxic NAPQI (a metabolite of acetaminophen)
NAPQI binds hepatocellular proteins
(see Acetaminophen Overdose: pathogenesis and clinical findings slide)
Drug-induced liver injury
Metabolism of drugs by the liver can produce reactive drug metabolites
Intracellular stress, mitochondrial injury, or immune response
Viral Hepatitis (i.e. HAV, HBV, HEV, HSV)
Acute infection or infection flare provokes an immune response against infected hepatocytes
Autoimmune Hepatitis
Autoimmune antibodies attack hepatocytes (see Auto-immune Hepatitis (AIH) slide)
Ischemia (i.e. from shock)
↓ O2 delivery to the liver
Hepatocellular hypoxia
Wilson’s Disease
Heritable mutation in the ATP7B gene
↓ Biliary excretion of copper
Hepatic copper accumulation injures hepatocytes (see Wilson’s Disease slide)
Accelerated rate of hepatocellular necrosis or apoptosis
Hepatocyte death exceeds regeneration such that liver function is compromised within a short amount of time
Acute Liver Failure
An illness of <26 weeks duration in the absence of pre-existing cirrhosis, characterized by INR ≥1.5 and evidence of altered mentation (hepatic encephalopathy)
Injured hepatocytes leak hepatic enzymes (AST, ALT, GGT) into circulation
↑ Liver enzymes
Hepatocellular inflammation
Stimulation of foregut
autonomic nerves
Right upper quadrant pain
↓ Toxin metabolism
Toxins build up and activate microglial cells (brain macrophage)
Oxidative stress and cerebral edema
Hepatic encephalopathy
Characteristic set of neuropsychiatric symptoms (see Hepatic Encephalopathy slide)
↓ Hepatocellular function and number
↓ Complement protein synthesis
↓ Ability to clear immune complexes and activate B cells
Accumulation of pigmented bilirubin
↓ Synthesis of coagulation factors
↑ INR
↓ Conjugation of bilirubin by the liver and ↓ transport into bile for excretion
↑ Serum bilirubin
Jaundice
Infection
Legend:
Pathophysiology
Mechanism
Sign/Symptom/Lab Finding
Complications
Published November 15, 2022 on www.thecalgaryguide.com
Foundations
Systems
Other Languages
Gastroenterology Liver Disorders Acute Liver Failure: Pathogenesis and clinical findings Acute Liver Failure: Pathogenesis and clinical findings