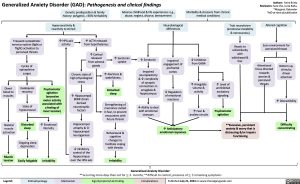
Generalized Anxiety Disorder (GAD): Pathogenesis and clinical findings
Authors: Keira Britto Reviewers: Sara Cho, Luiza Radu, *Margaret Oakander *MD at time of publication
Altered cognition
Scan environment for perceived threats
Genetic predisposition & family history: polygenic, >30% heritability
Adverse childhood & life experiences: e.g., abuse, neglect, divorce, bereavement
Morbidity & stressors from chronic medical conditions
Hypersensitivity & reactivity to stimuli
áHPA axis activity
Neurobiological differences
Trait neuroticism (emotional instability & nervousness)
Reacts to unfamiliarity with withdrawal & fear
áLevel of uninhibited excitatory signaling
Psychomotor agitation
Frequent sympathetic nervous system (fight or flight) activation to perceived threats
Cycles of epinephrine surges
Inadequate recovery
State of hyperarousal
Disturbed sleep
Ongoing sleep deprivation
Easily fatigable
áACTH released from hypothalamus
áCortisol released from adrenal glands
áSerotonin uptake
âSerotonin Impaired
neuroplasticity &âcomplexity of synaptic connections in amygdala & hippocampus
âAbility to deal with emotional stressors
Impaired engagement of prefrontal cortex
âRegulation of emotional reactions
áAnticipatory emotional responses
âInhibition from GABA
áAmygdala volume & activity
áFear & anxiety circuits
Attentional focus directed towards worries & perceived threats
Divert blood to muscles
Skeletal muscle activation
Muscle tension
Psychomotor agitation (excessive motor activity associated with a feeling of inner tension)
áEmotional intensity
Chronic state of high physiological stress
âHippocampal BDNF (brain derived neurotrophic factor)
Hippocampal atrophy &â hippocampal neurogenesis
â Inhibitory control of the hippocampus over the HPA axis
áAlertness & wakefulness
Disturbed sleep
Strengthening of memories rooted in fear, to prevent encounters with future threats
Behavioural & cognitive changes to facilitate coping with threats
Irritability
**Excessive, persistent
Bottom up, stimulus driven attention
áDistractibility
Difficulty concentrating
anxiety & worry that is distressing &/or impairs functioning
Irritability
Generalized Anxiety Disorder:
**occurring more days than not for ≥ 6 months; **difficult to control; presence of ≥ 3 remaining symptoms
Legend:
Pathophysiology
Mechanism
Sign/Symptom/Lab Finding
Complications
Published July 21, 2024 on www.thecalgaryguide.com