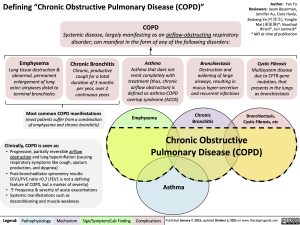
Defining “Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD)”
Author: Yan Yu Reviewers: Jason Baserman, Jennifer Au, Ciara Hanly, Zesheng Ye (叶泽生), Yonglin Mai (麦泳琳)*, Naushad Hirani*, Juri Janovcik* * MD at time of publication
Cystic Fibrosis
Multisystem disease due to CFTR gene mutation, that presents in the lungs as bronchiectasis
Bronchiectasis, Cystic Fibrosis, etc
COPD
Systemic disease, largely manifesting as an airflow-obstructing respiratory disorder; can manifest in the form of any of the following disorders:
Emphysema
Lung tissue destruction & abnormal, permanent enlargement of lung acini: airspaces distal to terminal bronchioles
Chronic Bronchitis
Chronic, productive cough for a total duration of 3 months per year, over 2 continuous years
Asthma
Asthma that does not
remit completely with treatment (thus, chronic airflow obstruction) is defined as asthma-COPD overlap syndrome (ACOS)
Emphysema
Bronchiectasis
Destruction and widening of large airways, resulting in mucus hyper-secretion and recurrent infections
Chronic Bronchitis
Most common COPD manifestations
(most patients suffer from a combination of emphysema and chronic bronchitis)
Clinically, COPD is seen as:
• Progressive, partially reversible airflow obstruction and lung hyperinflation (causing respiratory symptoms like cough, sputum production, and dyspnea)
• Post-bronchodilator spirometry results: FEV1/FVC ratio <0.7 (FEV1 is not a defining feature of COPD, but a marker of severity)
• ↑ frequency & severity of acute exacerbations
• Systemic manifestations such as
deconditioning and muscle weakness
Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD)
Asthma
Legend:
Pathophysiology
Mechanism
Sign/Symptom/Lab Finding
Complications
Published January 7, 2013, updated October 5, 2021 on www.thecalgaryguide.com