Secondary Polycythemia: Pathogenesis
Authors: Noriyah Al Awadhi, Yan Yu, Peter Duggan* Reviewers: Crystal Liu, Kara Hawker, Paul Ratti, Man-Chiu Poon*, Lynn Savoie* * MD at time of initial publication
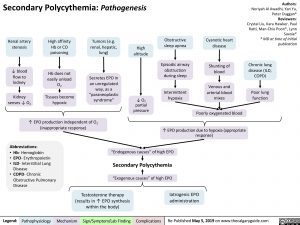
Chronic lung disease (ILD, COPD)
Poor lung function
Renal artery stenosis
↓ blood flow to kidney
Kidney senses ↓ O2
High affinity Hb or CO poisoning
Hb does not easily unload O2
Tissues become hypoxic
Tumors (e.g. renal, hepatic, lung)
Secretes EPO in an unregulated way, as a “paraneoplastic syndrome”
High altitude
Obstructive sleep apnea
Episodic airway obstruction during sleep
Intermittent hypoxia
Cyanotic heart disease
Shunting of blood
Venous and arterial blood mixes
Poorly oxygenated blood
↓ O2 partial pressure
↑ EPO production independent of O2 (inappropriate response)
↑ EPO production due to hypoxia (appropriate response)
Abbreviations:
• Hb- Hemoglobin
• EPO- Erythropoietin • ILD- Interstitial Lung
Disease
• COPD- Chronic
Obstructive Pulmonary Disease
“Endogenous causes” of high EPO
Secondary Polycythemia
“Exogenous causes” of high EPO
Testosterone therapy Iatrogenic EPO (results in ↑ EPO synthesis administration
within the body)
Legend:
Pathophysiology
Mechanism
Sign/Symptom/Lab Finding
Complications
Re-Published May 5, 2019 on www.thecalgaryguide.com