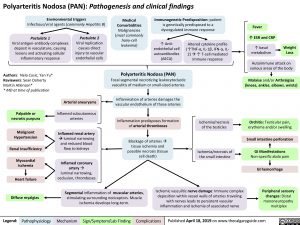
Polyarteritis Nodosa (PAN): Pathogenesis and clinical findings
Environmental triggers
Infectious/viral agents (commonly Hepatitis B)
Medical Comorbidities Malignancies (most commonly hairy-cell leukemia)
Immunogenetic Predisposition: patient is genetically predisposed to a dysregulated immune response
Fever
↑ ESR and CRP
Postulate 1
Viral antigen-antibody complexes deposit in vasculature, causing lesions and activating cellular inflammatory response
Authors: Nela Cosic, Yan Yu* Reviewers: Sean Doherty Martin Atkinson*
* MD at time of publication
Palpable or necrotic purpura
Malignant Hypertension
Renal Insufficiency
Myocardial ischemia
Heart failure Diffuse myalgias
Postulate 2
Viral replication causes direct injury to vascular endothelial cells
↑ Anti- endothelial cell autoantibodies (AECA)
Altered cytokine profile (↑TNF-α, IL-1β, IFN-α, IL- 2)à↑ T-cell mediated immune response
Weight metabolism Loss
Autoimmune attack on various areas of the body
Malaise and/or Arthralgias (knees, ankles, elbows, wrists)
Orchitis: Testicular pain, erythema and/or swelling
Small intestine perforation GI Manifestations
Non-specific abdo pain
GI hemorrhage
Peripheral sensory changes: Distal mononeuropathy
multiplex
Polyarteritis Nodosa (PAN)
Focal segmental necrotizing leukocytoclastic vasculitis of medium or small-sized arteries
Inflammation of arteries damages the vascular endothelium of those arteries
Inflammation predisposes formation of arterial thromboses
Blockage of arteriesà tissue ischemia and possible necrosis (tissue cell death)
↑ basal
Arterial aneurysms
Inflamed subcutaneous arteries
Inflamed renal artery
àluminal narrowing and reduced blood flow to kidneys
Inflamed coronary artery à luminal narrowing, occlusion, thromboses
Segmental inflammation of muscular arteries, stimulating surrounding nociceptors. Muscle ischemia develops long-term.
Ischemia/necrosis of the testicles
Ischemia/necrosis of the small intestine
Ischemic vasculitic nerve damage: Immune complex deposition within vessel walls of arteries traveling with nerves leads to persistent vascular inflammation and ischemia of associated nerve
Legend:
Pathophysiology
Mechanism
Sign/Symptom/Lab Finding
Complications
Published April 18, 2019 on www.thecalgaryguide.com
Foundations
Systems
Other Languages
Rheumatology Vasculitis Polyarteritis Nodosa (PAN): Pathogenesis and Clinical Findings Polyarteritis Nodosa (PAN): Pathogenesis and Clinical Findings