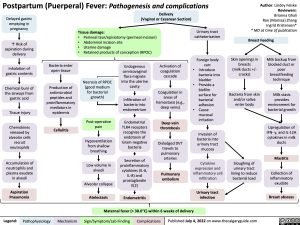
Postpartum (Puerperal) Fever: Pathogenesis and complications
Author: Lindey Felske Reviewers: Brianna Ghali Ran (Marissa) Zhang Ingrid Kristensen* * MD at time of publication
Breast Feeding
Delayed gastric emptying in pregnancy
↑ Risk of aspiration during delivery
Inhalation of gastric contents
Chemical burn of the airways from gastric acid
Tissue injury
Chemokines released by alveolar cells recruit neutrophils
Accumulation of neutrophils and plasma exudate in alveoli
Aspiration Pneumonia
Delivery
(Vaginal or Cesarean Section)
Tissue damage:
Urinary tract catheterization
Foreign body can: Introduce
bacteria into bladder Provide a biofilm surface for bacterial adhesion Cause mucosal irritation
Invasion of bacteria into urinary tract mucosa
• • • •
Perineal tear/episiotomy (perineal incision) Abdominal incision site
Uterine damage
Retained products of conception (RPOC)
Bacteria enter open tissue
Production of antimicrobial peptides and proinflammatory mediators in epidermis
Cellulitis
Necrosis of RPOC (good medium for bacterial growth)
Post-operative pain
Hypoventilation from shallow breathing
Low volume in alveoli
Alveolar collapse
Endogenous cervicovaginal flora migrate into the uterine cavity
Infiltration of bacteria into endometrium
Endometrial TLR4 receptors recognize the endotoxin of Gram-negative bacteria
Secretion of proinflammatory cytokines (IL-6, IL-8) and prostaglandin E(2)
Activation of coagulation cascade
Coagulation in areas of hemostasis (e.g., deep veins)
Deep vein thrombosis
Dislodged DVT travels to pulmonary arteries
Pulmonary embolism
• •
•
Skin openings in breasts (milk ducts +/- cracks)
Bacteria from skin and/or saliva enter body
Milk backup from blocked duct or poor breastfeeding technique
Milk stasis provides environment for bacterial growth
Upregulation of IFN- γ, and IL-12A cytokines in milk ducts
Mastitis
Collection of inflammatory exudate
Breast abscess
Cytokine expression and inflammatory cell infiltration
Sloughing of
urinary tract lining to reduce bacterial load
Atelectasis
Maternal fever (> 38.0°C) within 6 weeks of delivery
Urinary tract infection
Endometritis
Legend:
Pathophysiology
Mechanism
Sign/Symptom/Lab Finding
Complications
Published July 4, 2022 on www.thecalgaryguide.com
The image part with relationship ID rId4 was not found in the file.
Foundations
Systems
Other Languages
Obstetrics Labor Postpartum (Puerperal) Fever: Pathogenesis and complications postpartum-puerperal-fever-pathogenesis-and-complications